Understanding student demographics is crucial for colleges' strategic planning and policy development. Campuses must innovate and adapt to remain sustainable and relevant. Demographics are not destiny, but they do play a significant role in shaping the size and composition of the student body. A decline in the number of high school graduates will inevitably lead to decreased enrollment, while an increase in nontraditional students will require institutions to adapt their services and programs to meet varied needs.
In recent years, there has been a notable increase in the enrollment of graduate degree programs. Therefore, institutional leaders must prioritize the support and well-being of these students. As many master's and doctoral degree seekers are typically older and choose online learning, there is an added urgency to provide them with flexible digital tools that effectively engage and accommodate their specific learning needs.
The traditional college student era is over, with only 40% of undergraduates aged 18-20 and a growing number of students aged 25 and up. This shift in demographics is reshaping the dynamics of higher education and presents challenges for institutional leaders. It is important to understand these shifts to appropriately recruit, engage, and retain students.
Diversity in higher education is an important and timely topic, as institutions, policymakers, and economists recognize the value of a skilled and diverse student body and workforce. Student body diversity is influenced by institutional characteristics, geographical setting, and local demographic composition.
To increase student diversity, institutions should consider their policies regarding ethnic/racial diversity, such as affirmative action or race-conscious admissions. Additionally, the increasing number of international students has an impact on student demographics, with 70.77% of international students in U.S. postsecondary institutions coming from Asia.
Understanding and responding to shifting student demographics is essential for institutions to stay agile and provide the best possible education and support for their students.
What You'll Learn

Student diversity and its impact on learning and career outcomes
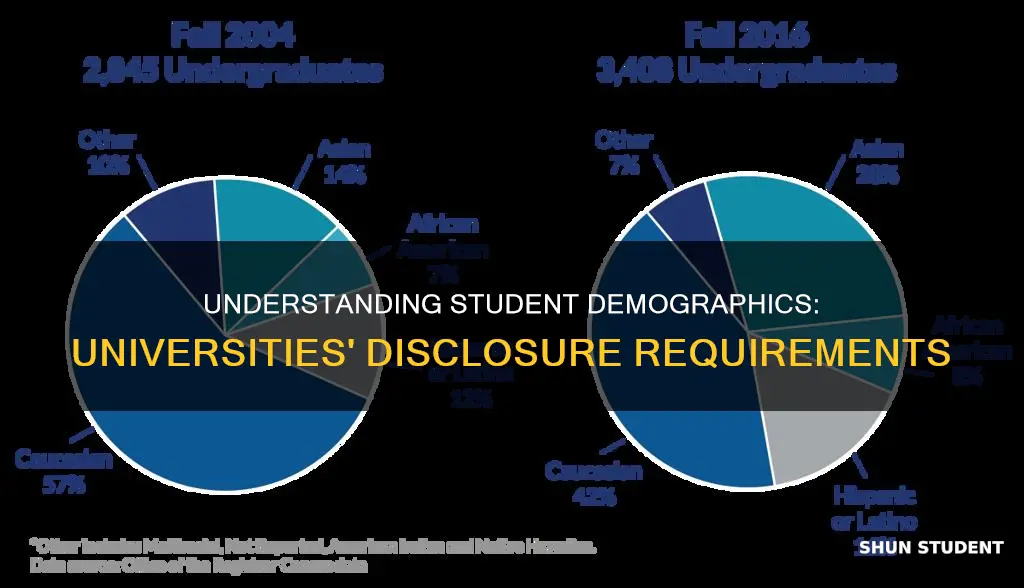
Diversity in the student body is an important aspect of higher education. In the US, around 40% of undergraduates are students of color, with White students making up 40.5% of the total undergraduate population as of 2023. Hispanic and Latino/a students are the second-largest group, at roughly 18% of the total undergraduate population.
The benefits of student diversity are felt in both the social and learning environments of colleges. Firstly, in terms of social benefits, a diverse student body promotes inclusivity and tolerance among students. It encourages students to appreciate differences, respect diverse perspectives, and develop intercultural competence, which are essential skills in an increasingly interconnected world. This can lead to a reduction in incidents of bullying, discrimination, and prejudice within the school environment.
Additionally, a diverse student body can positively impact the learning outcomes of students. Research has found that a higher degree of racial diversity in the classroom causes a statistically significant increase in the cumulative grade point average (GPA) at graduation. Specifically, replacing one White student with one minority student in a typical conference increases graduation GPA by an average of 0.024 σ. Diversity also improves the first-year grades of female students and affects the major choices of White students, who are more likely to take up majors in social sciences, history, and philosophy in more diverse classrooms.
Furthermore, students who attend diverse institutions tend to have more diverse friend groups, which can positively impact their social experience. Additionally, there is a positive correlation between attending a racially diverse institution and future earnings potential. This may be because graduates from diverse colleges are more attractive job candidates for companies with a global reach.
Colleges and universities play a crucial role in fostering a diverse environment, where students are exposed to worldviews and experiences different from their own. This enriches the overall learning experience and better prepares graduates for the globalized economy. To achieve this, institutions must recognize and address the unique needs of their diverse student body. For example, adult learners may have different demands, such as full-time employment and family caregiving, which institutions should consider when developing engagement and retention strategies.
In conclusion, student diversity has a positive impact on both the learning and career outcomes of students. It enhances the social experience, improves academic performance, and increases future earnings potential. Institutions that embrace and promote diversity are better equipped to support their students and prepare them for success in an increasingly globalized world.
Lesley University: Out-of-State Students' Support System
You may want to see also

The role of race and ethnicity in college admissions
Affirmative Action and Race-Conscious Admissions
Affirmative action, which has its roots in the Civil Rights Movement of the 1960s, is the practice of considering a student's background characteristics, such as race, when deciding on admission. This approach has been employed by selective colleges, acknowledging the unequal access to educational opportunities in the United States. However, critics argue that race-conscious admissions amount to racial discrimination, particularly harming White and Asian American students.
Supreme Court Rulings
The use of racial quotas in college admissions was deemed unconstitutional in the 1978 Supreme Court case, *Regents of the University of California v. Bakke*. The court ruled that such practices violate the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the equal protection clause of the 14th Amendment. Despite this, until June 2023, the Supreme Court had consistently allowed the consideration of race as a factor in admissions, citing the educational benefits of a diverse student body.
Public Opinion
Public opinion on this issue is divided. While a 2019 Pew Research Center survey found that 73% of American adults disapproved of colleges considering race or ethnicity in admissions, a more recent 2023 survey showed mixed sentiments, with half of adults disapproving and about one-third approving. Partisanship plays a role in these differing views, with Republicans more likely to see negative impacts on the fairness of the process and Democrats viewing it more positively in terms of ensuring equal opportunity.
Impact on Diversity and Representation
The impact of race-conscious admissions on campus diversity is significant. According to data, diversity in college enrollment has increased over time, with the representation of all racial and ethnic groups rising between 1980 and 2022, except for White students. The share of White students dropped from 81% in 1980 to 54% in 2020. During the same period, Hispanic and Latino/a representation increased from 4% to over 20%, while Black, Asian, and Pacific Islander populations also grew.
Benefits of Diversity in Higher Education
Research suggests that attending a racially diverse institution has a positive correlation with future earnings potential and family income. Students who attend diverse colleges can expect higher incomes, and diverse campuses benefit students socially and in their future careers. Additionally, having instructors from the same race improves Black students' performance and reduces their likelihood of dropping out.
Strategies for Diversity without Affirmative Action
Following the Supreme Court's ban on the use of race in admissions, colleges are exploring alternative strategies to promote diversity. Some institutions are reevaluating legacy admissions policies and athletic recruiting practices, which have historically advantaged White applicants. Other approaches include test-optional admissions, targeted student recruitment in diverse areas, and allocating a larger percentage of aid to need-based grants.
The debate surrounding the role of race and ethnicity in college admissions remains complex, with valid arguments on both sides. While the goal of promoting diversity and equal opportunity is widely supported, the means of achieving this goal are subject to ongoing legal and societal scrutiny.
Depression's Impact on University Students: Understanding the Challenge
You may want to see also

The changing demographics of college students
The changing face of college demographics in the US is challenging traditional ideas of the "typical" college student. Non-traditional students, aged 25 and older, now make up the majority of the post-secondary student population. This shift has been influenced by a range of factors, including the economic downturn of 2008, which led to people delaying starting families and a decline in the birth rate. The impact of these demographic changes on higher education is significant, with a projected 10-15% reduction in college enrolments by the end of the 2020s.
Racial Diversity
One of the most notable changes in college demographics is the increasing racial diversity of the student body. The number of students of colour has been steadily increasing, with around 40% of undergraduates identifying as students of colour. Hispanic and Latino/a students are the second largest group, making up around 18% of undergraduates, while Black students comprise approximately 11%, Asian students 6%, and Native American students less than 1%. This trend is expected to continue, with projections showing an 11% increase in first-time college attendees by 2029.
Gender Diversity
Women have outnumbered men in colleges and universities since 1979, and this trend continues. In 2022, 8.3 million women were enrolled in postsecondary institutions compared to 6.1 million men. Additionally, women have surpassed men in terms of advanced degrees, with 10.6 million American women holding master's degrees or higher, compared to 10.5 million men.
Non-Traditional Students
The rise of non-traditional students is reshaping higher education. These students often juggle full-time jobs and family commitments with their studies and have unique needs that must be addressed to ensure their success. Non-traditional students are also more likely to take evening and weekend classes and to utilise online learning, reflecting their busy schedules and the importance of flexibility in their studies.
Geographic Diversity
The geographic distribution of college students is also changing. There has been a shift towards the south and west of the US, with a decrease in the number of Northeastern non-Hispanic whites and an increase in Hispanic students from the Southwest. This shift has implications for college attendance rates, with higher education traditionally being more prevalent in the Northeast.
Malone University's Student Population: A Comprehensive Overview
You may want to see also

Strategies for increasing student diversity
Firstly, it is important to define what diversity means for your institution. Diversity can refer to many aspects of identity, such as race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, religion, disability, socioeconomic status, nationality, and academic discipline. Having clear and realistic diversity goals that align with your institution's vision, mission, and values is essential.
- Review policies and practices: Identify any potential biases or barriers that may hinder the recruitment and enrollment of diverse students. This includes examining admission criteria, financial aid policies, and affirmative action or holistic review methods to ensure fairness and equity.
- Expand outreach and recruitment efforts: Build relationships with a wider range of schools, community organizations, mentors, and alumni to attract diverse students. Utilize various platforms like social media, websites, and podcasts to showcase your diversity initiatives. Involve current students, faculty, and staff in sharing their stories and experiences with prospective students.
- Enhance support and retention strategies: Provide academic, social, emotional, and financial support for diverse students. Create a welcoming and inclusive campus culture that respects and celebrates diversity. Offer leadership, research, and study abroad programs to enhance their overall experience.
- Offer scholarships and financial aid: Reduce financial barriers, especially for international students and those from underrepresented backgrounds. Design scholarship programs to promote diversity and inclusion, targeting specific groups such as women, minorities, or underrepresented regions.
- Diversify partnerships: Collaborate with diverse higher education institutions, organizations, or agencies to facilitate student and staff exchanges, joint programs, and research initiatives. This will expand your network, increase visibility, and enhance your reputation.
- Conduct market research: Understand the needs, preferences, and expectations of your target markets to tailor your marketing and recruitment strategies effectively. Identify gaps and trends in your current and potential regions of recruitment to appeal to diverse groups of prospective students.
- Evaluate and improve: Regularly assess your strategies and outcomes to monitor their impact and effectiveness. Use feedback, surveys, and data analysis to identify strengths and weaknesses, making adjustments as needed to continuously improve.
By implementing these strategies, higher education institutions can increase student diversity, creating a more inclusive and enriching learning environment.
Financial Aid for International Students at University of Richmond
You may want to see also

The impact of demographics on college funding and resources
Demographic shifts in higher education have significant implications for college funding and resource allocation. As the traditional college student population declines, institutions must adapt their funding strategies and resource distribution to cater to the changing needs of a more diverse student body. Here are some key impacts of demographics on college funding and resources:
- Funding Allocation: Demographic changes can influence funding allocation decisions by colleges. For example, the increasing number of adult learners, who often have unique financial needs, may prompt colleges to allocate more funds towards financial aid and support services for this demographic group.
- Resource Allocation: Colleges need to allocate resources differently to cater to the diverse needs of their student body. For instance, with the rise in online learning, colleges may need to invest more in digital infrastructure and support to accommodate students who prefer flexible learning options.
- Diversity and Inclusion Initiatives: Demographic shifts emphasize the importance of diversity and inclusion initiatives. Colleges may need to allocate more funds towards programs and resources that foster an inclusive environment, ensuring that students from various backgrounds feel a sense of belonging on campus.
- Targeted Funding: Understanding the changing demographics of their student body allows colleges to target their funding more effectively. For example, with an increasing number of Hispanic and Latino/a students, colleges may allocate more funds towards programs and resources that cater to the specific needs and interests of this demographic group.
- Faculty Diversity: Demographic changes in the student body may also prompt colleges to reevaluate the diversity of their faculty. Investing in the recruitment and retention of a diverse faculty can enhance the overall diversity of the institution, creating a more inclusive learning environment.
- Scholarships and Financial Aid: Demographic shifts can influence the types of scholarships and financial aid offered by colleges. For instance, with a growing number of first-generation college students, institutions may create dedicated scholarships to support this demographic group.
- Part-Time Student Support: With a significant portion of students pursuing their studies part-time, colleges need to allocate resources to support these students effectively. This may include providing additional academic advising, flexible course options, and access to part-time employment opportunities on campus.
- Online Learning Resources: The increasing popularity of online learning, especially among younger students, calls for more investment in online resources and support services. Colleges need to ensure that online students have access to the same quality of resources as their on-campus counterparts.
- Community-Building Initiatives: Demographic changes may prompt colleges to initiate community-building initiatives to foster a sense of belonging among students. This can include creating digital communities, cultural clubs, and mentorship programs that cater to the diverse backgrounds and interests of the student body.
- Curriculum Development: Demographic shifts can influence curriculum development, ensuring that course content and teaching methods are relevant and inclusive for a diverse student population. This may involve incorporating diverse perspectives, addressing sensitive topics, and providing training to faculty on cultural competency.
In conclusion, understanding the impact of demographics on college funding and resources is crucial for institutions to adapt to the changing needs of their student body. By allocating funds and resources effectively, colleges can create an inclusive and supportive environment that enhances the overall educational experience for a diverse range of students.
Exploring Drexel University's Student Population
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, universities are not required to provide student demographics. However, they may choose to do so for transparency and accountability purposes, or to showcase their diversity and inclusion efforts.
Providing student demographics can help universities demonstrate their commitment to diversity and inclusion. It can also help them attract a wider range of students and improve their institutional reputation. Additionally, sharing student demographics can lead to increased government funding and support for universities.
Student demographics typically include information such as age, gender, race, ethnicity, and socio-economic background. It may also include information on first-generation students, international students, and students with disabilities.
Universities can collect student demographic information through various methods, including application forms, enrolment surveys, and periodic student surveys. It is important to ensure that data collection is done ethically and with student privacy in mind.







