The number of students enrolled at universities varies depending on the country, type of institution, and level of study. In the US, there were roughly 18 million students enrolled in colleges in 2022, with approximately 13.49 million enrolled in public colleges and a further 5.09 million enrolled in private colleges. This number is projected to remain relatively constant in the coming years.
In the academic year of 2022/23, around 20.3 million students were enrolled for undergraduate degrees in the US, a slight decrease from the previous year. Undergraduate enrollment has been on a downward trend since 2010, with a 7% decline from 2019 to 2022.
In the UK, the number of students enrolled at universities is different again. As an example, the University of Oxford had 23,985 students enrolled in the 2021-2022 academic year.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Total number of students enrolled in U.S. colleges | 18 million |
| Number of students enrolled in undergraduate programs | 15.2 million |
| Number of students enrolled in graduate programs | 3.1 million |
| Percentage of high school graduates enrolled in college | 62% |
| Percentage of 18-24-year-olds enrolled in postsecondary programs | 39% |
| Percentage of full-time students | 65% |
| Percentage of undergraduate students who are women | 55% |
| Percentage of undergraduate students who are men | 42% |
| Number of students enrolled in four-year public institutions | 7.6 million |
| Number of students pursuing a bachelor's degree | 8.5 million |
| Number of students pursuing an associate degree | 4.4 million |
| Number of students enrolled in graduate programs | 3.1 million |
| Number of students enrolled in online courses | 30% |
| Average age of full-time undergraduate students | 22.5 |
What You'll Learn

Undergraduate vs graduate enrolment
Undergraduate Enrolment
Undergraduate study is the first level of higher education and is typically pursued after secondary school. Undergraduate degrees include general education courses and courses focused on a chosen major. An undergraduate degree is usually completed in four years and often results in a bachelor's degree. In the US, undergraduate degrees can also result in associate's degrees, foundation degrees, higher national diplomas, diplomas of higher education, and national vocational qualifications.
Graduate Enrolment
Graduate study, also known as postgraduate study, is the next level of higher education after an undergraduate degree. Graduate degrees build on existing knowledge and allow students to develop expertise in a specific topic or field. Graduate degrees include master's degrees, postgraduate diplomas, and doctorate degrees. Graduate degrees are more specialised and focused on a particular area of study.
Differences in Enrolment
The enrolment numbers for undergraduate and graduate programs can vary. In the US, undergraduate enrollment has been declining since 2010, with approximately 15.2 million students enrolled in undergraduate programs in 2023. On the other hand, graduate enrollment has been increasing, with around 3.1 million graduate students in 2023. The application process for graduate programs is generally more complex than for undergraduate programs, and graduate programs often require students to apply to a specific program and work under a particular faculty member. Graduate programs also tend to be more expensive, especially when compared to the cost per credit of undergraduate programs.
Universities: Can They Force Students to Live on Campus?
You may want to see also

Enrolment by gender
Women have outnumbered men in colleges and universities since 1979. In fall 2023, over 10.1 million women were enrolled in college, compared to 7.2 million men. Women made up 55% of undergraduate students and nearly 60% of graduate students.
In fall 2021, female students made up 58% of total undergraduate enrollment (8.9 million students), and male students made up 42% (6.5 million students). Between 2010 and 2021, male enrollment decreased by 17% (from 7.8 million to 6.5 million students) and female enrollment decreased by 13% (from 10.2 million to 8.9 million students).
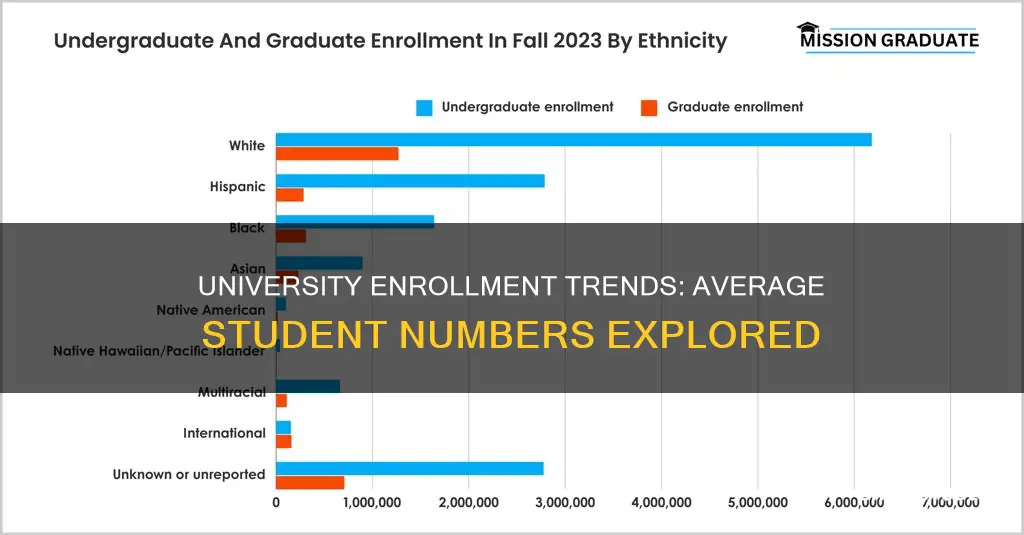
In 2021, 53% of undergraduate and graduate students were white. Of the 15.4 million undergraduate students enrolled in fall 2021, 7.8 million were White, 3.3 million were Hispanic, 1.9 million were Black, 1.1 million were Asian, 663,100 were of Two or more races, 107,000 were American Indian/Alaska Native, and 41,000 were Pacific Islander.
The number of female college attendees has nearly doubled since 1976, increasing by 82.9%. In 2022, about 62% of people who completed high school or earned a GED certificate immediately enrolled in college.
Pursuing Bachelor's: Four-Year University Completion Rates
You may want to see also

Enrolment by race/ethnicity
The number of students enrolled in colleges and universities varies across different racial and ethnic groups. In the US, the race and ethnicity of students influence their chances of earning a college degree. While college degrees are increasing among all racial and ethnic groups, white and Asian Americans are more likely to hold a college degree or earn one than Black, Hispanic, or Native Americans.
In 2011, more than 60% of the nation's 20.6 million college students were white, according to an estimate by the National Student Clearinghouse. By 2020, the share of white students had dropped by almost 9 percentage points to 52%, still a majority. During the same period, the share of Hispanic students grew from 14% to 21%, and the share of Black students remained constant at just under 14%. Asian students increased from 5% to 7% of the college population.
The demographic makeup of college campuses has changed over time, becoming less white and more Hispanic. The percentage of students of colour enrolled in colleges has increased from 15.36% in 1976 to 45.23% in 2022.
In the academic year 2022/23, there were around 20.3 million students enrolled for undergraduate degrees in the US, a slight decrease from the previous year. Of these students, 7.8 million were White, 3.3 million were Hispanic, 1.9 million were Black, 1.1 million were Asian, 663,100 were of Two or more races, 107,000 were American Indian/Alaska Native, and 41,000 were Pacific Islander.
Trends in undergraduate enrolment vary across racial and ethnic groups. Between 2010 and 2021, enrolment decreased for American Indian/Alaska Native, Pacific Islander, White, and Black students. In contrast, enrolment increased for students of Two or more races, Hispanic students, and Asian students.
Postbaccalaureate enrolment also shows variations across racial and ethnic groups. Between 2010 and 2021, enrolment decreased for American Indian/Alaska Native, White, and Pacific Islander students, while it increased for students of Two or more races, Hispanic students, and Asian students.
Enrolment Figures for East Carolina University Explored
You may want to see also

Enrolment by degree type
In the fall of 2023, there were about 15.2 million students enrolled in an undergraduate program in the US, with roughly 8.5 million pursuing a bachelor's degree and 4.4 million getting associate degrees. There were about 3.1 million graduate students in the US in 2023.
In the 2022/23 academic year, around 20.3 million students were enrolled for undergraduate degrees in the US, a slight decrease from the previous year, when 20.4 million students were enrolled as undergraduates.
In fall 2021, there were 3.2 million students enrolled at the postbaccalaureate level in degree-granting institutions in the US. Postbaccalaureate degree programs include master's and doctoral programs as well as professional degrees such as law and medicine.
Internships: Exclusive or Open to All?
You may want to see also

Enrolment by institution type
The type of institution a student chooses to attend can vary depending on factors such as cost, location, and program availability. Here is a breakdown of enrolment by institution type in the United States:
- Public Institutions: The majority of students in the US attend public colleges and universities. In 2022, there were around 13.49 million students enrolled in public institutions, making up about 72% of all postsecondary students. Public institutions tend to offer different tuition rates for in-state and out-of-state students, making them a more affordable option for many.
- Private Institutions: Private colleges and universities, which are funded by private donors and endowments, tend to be more expensive. In 2022, there were approximately 5.09 million students enrolled in private colleges, constituting about 27% of all postsecondary students. Private colleges often have the same tuition cost for all students, regardless of their state of residence.
- Two-Year vs Four-Year Institutions: Students can also choose between two-year and four-year degree programs. About 16.9% of new high school graduates enrol in two-year colleges, while 45.1% enrol in four-year programs. As of Fall 2022, there were 4.66 million students (or 25% of all students) attending two-year institutions, and 13.92 million students (or 75% of all students) attending four-year institutions.
- For-Profit vs Nonprofit Institutions: Within private institutions, there is a further distinction between for-profit and nonprofit colleges. Among postsecondary students attending private colleges, 80.77% attend nonprofit schools, while 19.23% attend for-profit institutions.
These enrolment numbers reflect the preferences and decisions of students and their families, influenced by various factors such as cost, program availability, and institutional reputation.
Ranking Students: The University Evaluation System Explored
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
In fall 2023, there were roughly 18.1 million students enrolled at a postsecondary institution in the US.
In fall 2023, about 15.2 million students were enrolled in an undergraduate program.
In fall 2023, there were about 3.1 million graduate students.
The average number of students enrolled at US universities has been decreasing over the past decade. In fall 2022, there were 20.3 million students enrolled for undergraduate degrees. In fall 2023, there were 18.1 million students enrolled at a postsecondary institution.







