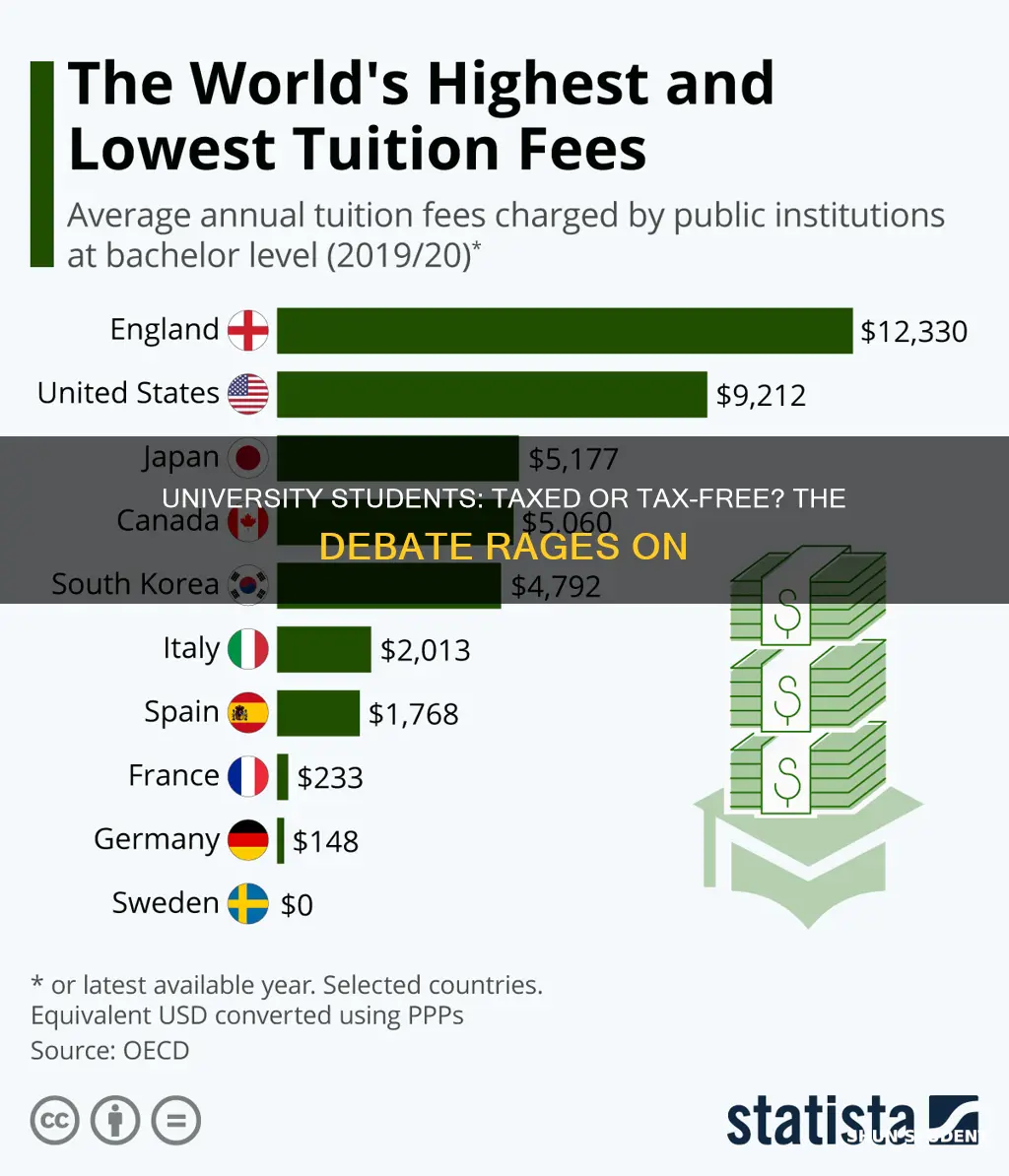
The question of whether university students should be taxed is a complex and controversial issue. While some argue that students should contribute to the cost of their education through taxation, others believe that it could create financial burdens for students, especially those from lower-income backgrounds. This debate often centers around the idea of equity, as it involves balancing the benefits of higher education with the potential impact on students' financial well-being. The discussion also raises questions about the role of government funding in supporting education and the potential consequences of implementing such a tax.
What You'll Learn
- Equity and Access: Taxing students can fund scholarships and aid, promoting equal access to education
- Infrastructure and Resources: Revenue can improve campus facilities and support services
- Research and Innovation: Student taxes can fund cutting-edge research, enhancing academic excellence
- Community Engagement: Taxes may support student-led initiatives, fostering a vibrant campus community
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Student fees can contribute to green initiatives, promoting a sustainable campus

Equity and Access: Taxing students can fund scholarships and aid, promoting equal access to education
The idea of taxing university students has sparked debates, but one compelling argument centers around equity and access to education. By implementing a student tax, governments can generate revenue to establish and expand scholarship programs and financial aid initiatives. This approach is particularly crucial in ensuring that higher education remains accessible to all, regardless of socioeconomic backgrounds.
The primary goal of this strategy is to promote equal opportunities for students from diverse financial circumstances. Many talented individuals might be deterred from pursuing higher education due to the associated costs, which can be a significant barrier for those from lower-income families. By providing financial support through scholarships and aid, the tax can help bridge this gap, allowing students to access the necessary resources for their academic pursuits. This, in turn, can lead to a more diverse and inclusive student body, fostering a rich learning environment.
Furthermore, the revenue generated from student taxation can be strategically allocated to create a robust financial aid system. This system could offer need-based grants, work-study programs, and low-interest loans, ensuring that students can afford their education without incurring overwhelming debt. Such an initiative would not only benefit individual students but also contribute to the overall economic stability of the country by producing a more educated and skilled workforce.
In addition, the tax can serve as a means to address the long-term financial implications of student debt. While some argue that student loans promote personal responsibility, the burden of debt can be overwhelming, especially for those facing economic challenges. By providing alternative funding mechanisms, the tax can help reduce the reliance on loans, thereby mitigating the risk of widespread financial strain among graduates.
In conclusion, taxing university students can be a strategic move to promote equity and access to education. It provides the necessary financial resources to establish comprehensive scholarship and aid programs, ensuring that financial barriers do not hinder students' academic aspirations. This approach not only benefits individual students but also contributes to a more inclusive and economically stable society.
Part-Time Research: University Access for Non-Students
You may want to see also

Infrastructure and Resources: Revenue can improve campus facilities and support services
The idea of taxing university students is a complex and controversial topic, but one potential argument in favor of such a measure is the potential to improve campus infrastructure and support services. By generating additional revenue, universities could enhance their facilities and provide better resources for students, which could have a positive impact on the overall educational experience.
One of the primary areas where this revenue could be directed is campus infrastructure. Many universities, especially older institutions, face challenges with aging buildings, outdated technology, and inadequate facilities. Taxing students could provide the necessary funds to address these issues. For example, the money could be used to renovate lecture halls, improve laboratory equipment, enhance library resources, and upgrade student housing. Well-maintained and modern infrastructure can create a more conducive learning environment, improve student satisfaction, and potentially attract more students to the university.
Additionally, the revenue could be allocated to enhance support services, which are crucial for student success and well-being. These services may include academic advising, career counseling, mental health support, and disability services. By investing in these areas, universities can ensure that students receive the guidance and assistance they need to excel academically and personally. Improved support services can lead to better student retention rates, higher graduation rates, and increased student satisfaction, all of which contribute to a more successful and thriving university community.
Furthermore, the additional funds could be used to develop and expand technology infrastructure. This includes upgrading internet connectivity, providing access to advanced software and research tools, and ensuring that all students have the necessary technological resources to support their studies. In today's digital age, robust technology infrastructure is essential for a modern university experience.
However, it is important to ensure that any tax imposed on students is carefully structured and transparent. The revenue should be utilized efficiently and with student welfare in mind. Regular audits and oversight can help maintain accountability and ensure that the funds are used for the intended purposes. With proper management, taxing university students could be a viable option to improve the overall quality of education and campus life.
Student Finance University Switch: Is It Possible?
You may want to see also

Research and Innovation: Student taxes can fund cutting-edge research, enhancing academic excellence
The idea of taxing university students to fund research and innovation is an intriguing concept that could have significant implications for academic excellence and the advancement of knowledge. While it may seem counterintuitive to impose taxes on students, the potential benefits to research and the overall educational experience are worth exploring. This approach could serve as a powerful mechanism to drive progress in various fields and foster a culture of innovation.
One of the primary advantages of utilizing student taxes for research funding is the direct allocation of resources to cutting-edge projects. University students, particularly those in STEM fields, often have access to the latest technologies and facilities, making them ideal candidates for contributing to innovative research. By taxing students, a dedicated fund can be established to support these initiatives, ensuring that the necessary resources are available to drive progress. This dedicated funding stream could be managed by academic institutions, allowing for efficient allocation based on research priorities and potential impact.
Furthermore, this approach encourages a sense of ownership and responsibility among students. When students contribute financially to their education and research endeavors, they become more invested in the outcomes. This sense of involvement can foster a culture of innovation, where students actively seek opportunities to contribute to cutting-edge research and develop a deeper understanding of the research process. As a result, the quality of education and research may improve, leading to more well-rounded and engaged students.
The impact of such a system could extend beyond individual institutions. With a network of universities collaborating and sharing resources, the collective research output could be substantial. This collaborative environment would facilitate knowledge exchange, accelerate research breakthroughs, and potentially lead to more rapid solutions for global challenges. Moreover, the funds generated could be used to attract top researchers and provide them with the necessary resources to pursue their innovative ideas, further enhancing the quality of research.
In conclusion, taxing university students to fund research and innovation presents a unique opportunity to enhance academic excellence and drive progress. By providing dedicated financial support, students can actively contribute to cutting-edge projects, fostering a culture of innovation. This approach has the potential to create a positive feedback loop, where improved research leads to better educational experiences, and ultimately, a more knowledgeable and engaged student body. While the idea may require careful implementation and consideration of alternative funding sources, the benefits to research and education could be transformative.
Understanding Student Loans at Indiana University
You may want to see also

Community Engagement: Taxes may support student-led initiatives, fostering a vibrant campus community
University students, often seen as the future leaders and innovators, can greatly benefit from a unique form of community engagement: the idea of taxation. While the concept of taxing students might seem counterintuitive, it presents an opportunity to empower students and create a more vibrant and active campus environment. Here's how this approach can be both beneficial and engaging:
Funding Student-Led Projects: One of the primary advantages of taxing students is the potential to provide a dedicated funding source for student-led initiatives. Many universities have a plethora of talented students with innovative ideas, but they often lack the financial resources to bring their visions to life. A small tax, perhaps in the form of a student levy, can be implemented to support these projects. This could range from funding cultural events and art exhibitions to supporting research groups and community service projects. By giving students the power to decide how this money is spent, it encourages active participation and a sense of ownership within the campus community.
Building a Sense of Community: Taxes can serve as a powerful tool to foster a stronger sense of community among students. When students are involved in the decision-making process regarding their campus life, they become more engaged and invested in the university's well-being. For instance, a student tax could be used to enhance common areas, such as libraries, student centers, and recreational facilities. These improved spaces would then become hubs for social interaction, collaboration, and community-building activities. As students contribute to the development of these shared environments, they are more likely to feel a deeper connection to their university, leading to increased satisfaction and a more vibrant campus culture.
Encouraging Leadership and Responsibility: Implementing a tax system specifically for students can also promote leadership skills and a sense of responsibility. Student representatives can be elected or appointed to manage the allocated funds, ensuring transparency and accountability. This process teaches students valuable skills in financial management, decision-making, and community engagement. Moreover, it empowers students to take an active role in shaping their university experience, fostering a culture of leadership and civic engagement from a young age.
Long-Term Benefits for the University: The impact of student taxation extends beyond the immediate campus community. By investing in student-led initiatives and campus improvements, universities can enhance their reputation and attract a wider pool of prospective students. A vibrant, active campus with a strong sense of community can become a selling point for the institution. Additionally, the skills and experiences gained through student-led projects can contribute to the development of well-rounded graduates, better prepared for the challenges and opportunities of the real world.
In conclusion, taxing university students is not merely about generating revenue but about empowering a generation of leaders and innovators. It provides an avenue for students to take charge of their campus environment, fostering a sense of community and ownership. With careful implementation and student involvement, this approach can lead to a more vibrant, engaged, and successful university experience.
McNeese State University's Student Enrollment Figures Revealed
You may want to see also

Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Student fees can contribute to green initiatives, promoting a sustainable campus
The idea of taxing university students is a complex and often controversial topic, but one aspect that can be explored is the potential for student fees to drive sustainability and environmental initiatives on campus. By allocating a portion of student fees towards green projects, universities can foster a culture of environmental responsibility and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Student fees, when directed towards sustainability, can have a significant impact on the environmental footprint of a university. These funds can be utilized to implement and maintain eco-friendly infrastructure, such as solar panels, wind turbines, or efficient waste management systems. For instance, installing solar panels on campus buildings can reduce the reliance on non-renewable energy sources, thus decreasing carbon emissions and promoting a cleaner environment. Similarly, investing in efficient waste management systems can encourage recycling and composting, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills.
Moreover, student fees can facilitate the development of green spaces and promote biodiversity. Universities can allocate funds to create and maintain gardens, parks, or green roofs, providing students with a peaceful natural environment for study and relaxation. These green spaces not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the campus but also contribute to improved air quality, reduced urban heat island effects, and the preservation of local ecosystems.
In addition to physical infrastructure, student fees can support educational and research programs focused on sustainability. This includes funding workshops, seminars, and awareness campaigns to educate students about environmental issues and sustainable practices. By empowering students with knowledge and skills, universities can foster a generation of environmentally conscious individuals who can drive positive change beyond campus boundaries.
By embracing the concept of taxing students for sustainability, universities can lead by example, demonstrating a commitment to environmental responsibility. This approach not only benefits the immediate campus community but also contributes to a global effort to combat climate change and promote a greener, more sustainable world. It encourages students to take an active role in shaping a better future, where education and environmental stewardship go hand in hand.
Track Team Triumphs: Corban University's Student Athletes
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The taxation of university students is a complex issue and a topic of ongoing debate. While some argue that students should be exempt from taxes as they are investing in their future through education, others suggest that a small tax could help fund student services and infrastructure. The decision to tax students should consider factors like the cost of education, the financial burden on students, and the potential benefits to the university community.
One argument is that taxing students can help generate revenue to improve the overall university experience. This revenue could be used to enhance facilities, provide better support services, and potentially reduce tuition fees, making education more accessible. Additionally, a tax could encourage students to make more informed financial decisions and develop a sense of financial responsibility.
Yes, there are concerns about the financial burden on students, especially those from lower-income backgrounds. Taxing students might discourage those who are already struggling financially, potentially leading to increased debt and long-term financial strain. It could also impact enrollment rates and student retention, as some may choose to pursue alternative educational paths or delay their studies.
Tax revenue from students can be utilized to enhance the university's infrastructure, including libraries, laboratories, and sports facilities. It can also fund student support services such as counseling, career guidance, and academic advising. Additionally, the money can be used to improve the overall learning environment, provide scholarships or grants, and facilitate research opportunities, ultimately benefiting the student body.
Absolutely. Universities can explore various funding options, such as government grants, corporate sponsorships, and alumni donations. They can also implement cost-saving measures, optimize resource allocation, and seek efficiency improvements. Diversifying funding sources and exploring innovative financing models can help reduce the reliance on student taxation while still meeting the financial needs of the institution.







