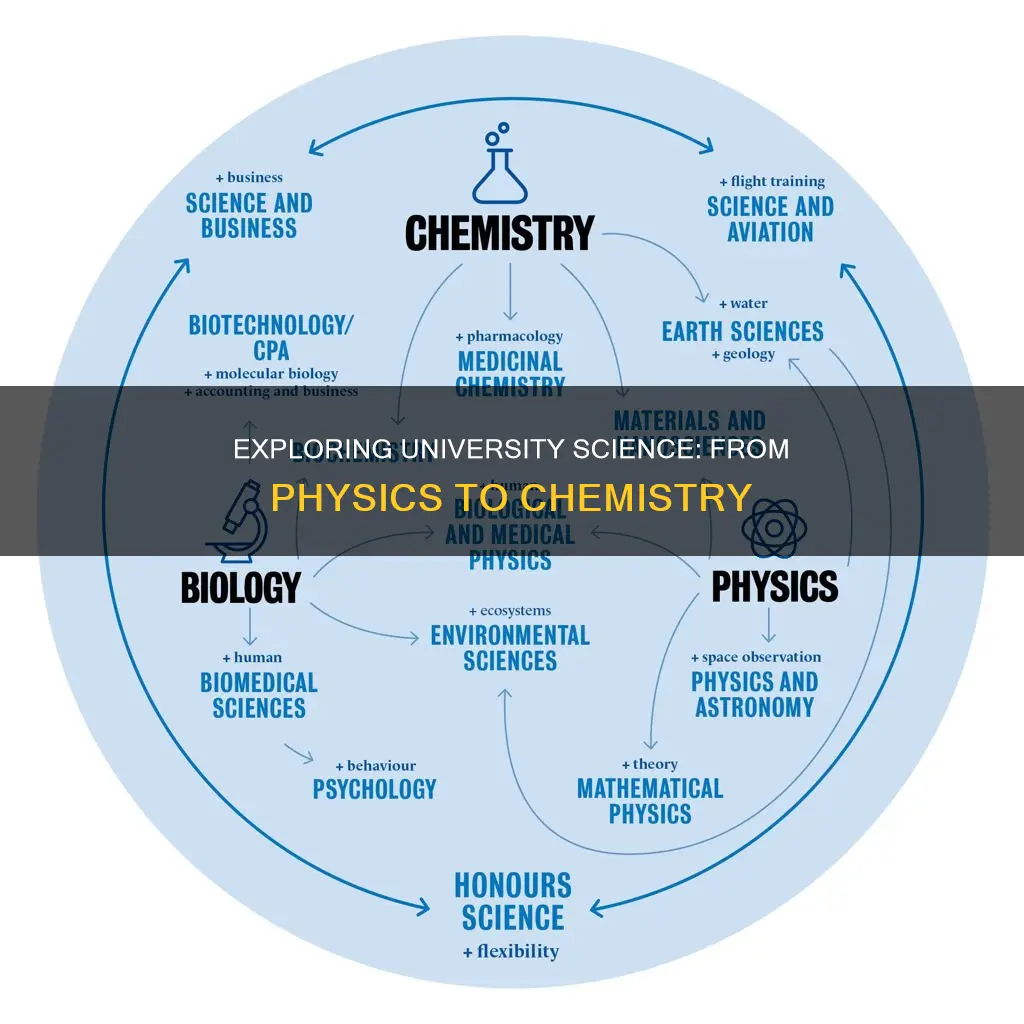
University offers a wide range of opportunities for science students to explore and specialize in various fields. From biology and chemistry to physics and astronomy, students can delve into the fundamental principles of the natural world. They can also study environmental science, focusing on the intricate relationships between living organisms and their surroundings. Additionally, students can choose to study computer science, delving into the world of algorithms and programming, or delve into the fascinating realm of neuroscience, exploring the complexities of the human brain. The possibilities are vast, allowing students to tailor their education to their interests and career aspirations.
What You'll Learn
- Biology: Cell biology, genetics, ecology, evolution, and physiology
- Chemistry: Organic, inorganic, physical, analytical, and environmental chemistry
- Physics: Mechanics, electromagnetism, quantum, relativity, and astrophysics
- Earth Sciences: Geology, meteorology, oceanography, and environmental science
- Computer Science: Programming, algorithms, data structures, AI, and cybersecurity

Biology: Cell biology, genetics, ecology, evolution, and physiology
Biology is a captivating field of study that delves into the intricate workings of life, offering a comprehensive understanding of the natural world. For science students, a university biology program provides a wealth of knowledge and skills, enabling them to explore the fundamental principles and processes that govern living organisms. Here's an overview of some key areas of focus within biology:
Cell Biology: This discipline focuses on the basic unit of life, the cell. Students will learn about cell structure, function, and metabolism, including the intricate mechanisms that enable cells to carry out essential life processes. From understanding the role of organelles to studying cell division and differentiation, cell biology provides insights into how cells maintain homeostasis and respond to their environment. It forms the foundation for comprehending the complexity of multicellular organisms.
Genetics: The study of genetics involves unraveling the mysteries of heredity and variation. Students will explore how genetic information is stored, transmitted, and expressed. Topics may include DNA structure and function, gene expression, inheritance patterns, and genetic mutations. Understanding genetics is crucial for deciphering the mechanisms of evolution, developing medical treatments, and even predicting and managing genetic disorders.
Ecology: Ecology examines the relationships between organisms and their environment. Biology students will investigate how organisms interact with each other and their surroundings, including the flow of energy and materials through ecosystems. This field covers topics such as population dynamics, community interactions, and the impact of environmental changes on species. Ecologists often study habitats, food webs, and the delicate balance that sustains biodiversity.
Evolution: Evolution is a cornerstone of biology, providing a historical perspective on the diversity of life. Students will learn about the mechanisms of evolution, including natural selection, genetic drift, and speciation. By studying the fossil record and comparative anatomy, they can trace the evolutionary history of various species. Understanding evolution is essential for grasping the interconnectedness of life forms and predicting how organisms adapt to changing environments.
Physiology: This branch of biology focuses on the functions of biological systems and organs. Students will explore how the human body maintains homeostasis, from the intricate workings of the cardiovascular system to the complex processes of digestion and respiration. Physiology also covers the chemical and physical processes that occur at the cellular level, providing insights into how the body responds to internal and external stimuli. Understanding physiology is vital for developing treatments for various medical conditions.
University biology programs often provide a well-rounded education, allowing students to choose electives or specialize in specific areas of interest. This flexibility enables students to tailor their studies to their passions, whether it's delving into the molecular biology of diseases, exploring the conservation of endangered species, or investigating the evolutionary history of ancient organisms. The study of biology equips students with a deep understanding of the natural world, fostering critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and a scientific mindset that can be applied to various real-world challenges.
The Procrastination Puzzle: Unlocking University Students' Delay Tactics
You may want to see also

Chemistry: Organic, inorganic, physical, analytical, and environmental chemistry
The field of chemistry offers a vast array of specializations for science students at the university level, each with its own unique focus and applications. Here, we delve into the various branches of chemistry, providing an overview of the key areas of study.
Organic Chemistry: This branch of chemistry is a cornerstone of many scientific disciplines. Organic chemists study the structure, properties, and reactions of carbon-containing compounds, which are fundamental to understanding life processes. Students will learn about the synthesis and analysis of organic molecules, including the identification of functional groups and the study of reaction mechanisms. Organic chemistry is essential for fields like pharmaceuticals, where the design and development of new drugs rely heavily on understanding molecular behavior. It also plays a crucial role in materials science, contributing to the creation of new polymers and plastics.
Inorganic Chemistry: Inorganic chemistry focuses on the behavior and properties of inorganic compounds, which are essential in various industries. Students will explore the synthesis, structure, and reactivity of inorganic materials, including metals, ceramics, and semiconductors. This field is vital for developing new technologies, such as advanced electronics, energy storage systems, and catalysts. Inorganic chemists often work on creating materials with specific properties, such as high-temperature superconductors or materials for solar cells, contributing to advancements in renewable energy and electronics.
Physical Chemistry: Physical chemistry bridges the gap between physics and chemistry, offering a more quantitative approach to understanding chemical systems. It involves the study of the physical properties of matter and the underlying principles that govern chemical reactions. Students will delve into thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, and statistical mechanics, gaining a deep understanding of the fundamental forces that drive chemical processes. This field is crucial for developing new materials, improving chemical processes, and advancing our knowledge of chemical reactions at the molecular level.
Analytical Chemistry: Analytical chemists are responsible for the precise measurement and identification of chemical substances. This field involves the development and application of techniques to separate, identify, and quantify components in a sample. Students will learn about various analytical methods, such as chromatography, spectroscopy, and electrochemistry, which are essential tools in quality control, environmental monitoring, and pharmaceutical research. Analytical chemistry plays a critical role in ensuring product safety, environmental protection, and the development of new materials.
Environmental Chemistry: Environmental chemistry focuses on the chemical processes occurring in the natural environment, addressing issues related to pollution, climate change, and sustainability. Students will study the sources, transport, and effects of pollutants, as well as the development of strategies to mitigate environmental problems. This field is crucial for understanding and addressing environmental challenges, such as water and air pollution, soil contamination, and the impact of human activities on ecosystems. Environmental chemists often work on projects related to renewable energy, waste management, and the development of green technologies.
Humboldt State University: Enrollment Figures and Trends
You may want to see also

Physics: Mechanics, electromagnetism, quantum, relativity, and astrophysics
Physics is a captivating field of study that delves into the fundamental principles governing the universe, offering a comprehensive understanding of the natural world. Within the realm of physics, students can explore various specialized areas, each contributing unique insights to our comprehension of the cosmos. One of the core branches is mechanics, which examines the motion and behavior of objects, from the smallest particles to massive celestial bodies. This field involves the study of classical mechanics, delving into concepts like Newton's laws of motion, energy conservation, and the principles of dynamics. Understanding these concepts is crucial for predicting and explaining the movement of everything from vehicles to planets.
Electromagnetism is another pivotal area within physics, focusing on the interplay between electric and magnetic fields. This branch explores how these fields interact with matter, leading to phenomena such as electric currents, magnetic forces, and electromagnetic waves. Students can study the behavior of charged particles, the principles of electromagnetic induction, and the propagation of light, all of which have practical applications in technology and everyday life.
Quantum physics takes the study of the microscopic world to a deeper level. It introduces students to the behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic levels, where classical physics falls short. Here, students encounter concepts like wave-particle duality, quantum superposition, and the uncertainty principle, which challenge our intuition about the physical world. Understanding quantum mechanics is essential for advancements in technology, from quantum computing to the development of advanced materials.
The theory of relativity, proposed by Albert Einstein, revolutionized our understanding of space and time. This branch of physics explores the relationship between gravity, space, and time, offering a more accurate description of the universe than classical physics. Students can delve into special and general relativity, learning how gravity affects the path of light and the behavior of objects in extreme conditions. Relativity has profound implications for astrophysics and our understanding of the cosmos.
Astrophysics combines physics with astronomy, providing a comprehensive view of the universe. Students in this field study the physical processes that occur in celestial bodies, such as stars, galaxies, and black holes. They explore topics like stellar evolution, galactic dynamics, and the origins of the universe. Astrophysics also involves understanding the fundamental forces and particles that shape the cosmos, contributing to our knowledge of the universe's evolution and its most extreme phenomena.
Exploring Western Washington University's Student Population
You may want to see also

Earth Sciences: Geology, meteorology, oceanography, and environmental science
Earth Sciences encompass a broad range of disciplines that focus on understanding our planet's complex systems and processes. These fields are essential for comprehending the natural world and addressing environmental challenges. Here's an overview of the key areas of study within Earth Sciences:
Geology: Geology is the study of the Earth's solid features, including its structure, composition, and history. Geology students delve into the formation and evolution of the Earth's crust, examining rocks, minerals, and geological processes. They learn about tectonic plate movements, earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the geological history of our planet. Fieldwork is a crucial part of geology, where students collect samples, map geological formations, and conduct research in various environments. This field offers a deep understanding of the Earth's structure and provides insights into natural resource exploration, environmental hazards, and the history of our planet.
Meteorology: Meteorology is the scientific study of the atmosphere and weather systems. Students in this field learn about the physical and chemical processes that drive weather patterns and climate. They analyze atmospheric conditions, study air masses, and understand the principles of weather forecasting. Meteorologists use advanced technology and data analysis to predict weather events, track storms, and study climate change. This discipline is vital for understanding and mitigating the impacts of extreme weather, such as hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves, and it also contributes to the development of sustainable environmental practices.
Oceanography: Oceanography is a multidisciplinary field that explores the oceans and their interactions with the Earth's systems. Students investigate the physical, chemical, and biological aspects of marine environments. This includes studying ocean currents, marine ecosystems, marine biology, and the impact of human activities on ocean health. Oceanographers may conduct research on topics like marine biodiversity, ocean acidification, and the effects of climate change on marine life. The field also involves exploring the deep sea, studying marine geology, and understanding the complex relationships between the ocean and the atmosphere.
Environmental Science: Environmental science integrates knowledge from various disciplines to study the natural environment and its interactions with human societies. Students examine the impact of human activities on ecosystems, pollution, and resource management. This field focuses on finding solutions to environmental problems, such as sustainable development, conservation, and pollution control. Environmental scientists may work on projects related to renewable energy, waste management, ecosystem restoration, and policy development. It involves understanding ecological processes, environmental chemistry, and the social and economic factors influencing environmental sustainability.
These Earth Sciences disciplines offer a comprehensive understanding of our planet's systems and provide practical knowledge to address environmental challenges. Students can specialize in specific areas or gain a broad foundation in these fields, contributing to scientific research, environmental management, and the development of sustainable practices.
International Students at Howard University: Who Gets Accepted?
You may want to see also

Computer Science: Programming, algorithms, data structures, AI, and cybersecurity
Computer Science is a fascinating and rapidly evolving field that offers a wide range of opportunities for students interested in technology and problem-solving. It encompasses various disciplines, each focusing on different aspects of computing and information technology. For science students, delving into computer science can open doors to exciting career paths and provide a solid foundation in the digital world. Here's an overview of some key areas of study within this field:
Programming is at the heart of computer science. It involves learning different programming languages, which are the tools used to instruct computers to perform specific tasks. Students will acquire skills in languages like Python, Java, C++, or JavaScript, each with its own syntax and applications. From web development to software engineering, programming forms the basis of creating functional and efficient software systems. Students will learn to write clean, structured code, debug programs, and understand the principles of software development.
Algorithms and data structures are fundamental concepts in computer science. Algorithms are step-by-step procedures to solve a problem or perform a computation, while data structures are ways to organize and store data efficiently. Students will study various algorithms, including sorting and searching algorithms, and learn how to analyze their time and space complexity. Understanding data structures like arrays, linked lists, trees, and graphs is crucial for optimizing code and solving complex problems. This knowledge is essential for developing efficient software and systems.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a captivating branch of computer science that focuses on creating intelligent machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. Students will explore machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and expert systems. They will learn to develop algorithms that can learn and make predictions from data, enabling machines to recognize patterns, understand language, and make decisions. AI has numerous applications, from virtual assistants and self-driving cars to medical diagnosis and financial analysis.
Cybersecurity is an increasingly vital field in the digital age, as it deals with protecting computer systems, networks, and sensitive information from potential threats and attacks. Computer science students will study cryptography, network security, and ethical hacking to understand how to secure data and systems. They will learn about various cyber threats, such as malware, phishing, and social engineering, and develop strategies to prevent and mitigate these risks. Cybersecurity professionals are in high demand to ensure the safety and privacy of digital information.
In summary, computer science offers a diverse range of studies for science students, from the foundational skills of programming and algorithm design to the cutting-edge fields of AI and cybersecurity. It equips students with practical knowledge and problem-solving abilities, enabling them to contribute to the ever-growing digital landscape. With its numerous applications and career prospects, computer science is an excellent choice for students seeking to make a meaningful impact in the technology sector.
Exploring the Student Population at University of West London
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
In a science degree, students typically study a combination of foundational and specialized subjects. Core areas include physics, chemistry, biology, mathematics, and often, a specific field of interest within the sciences, such as astronomy, geology, or environmental science. These subjects provide a strong foundation in scientific principles and methodologies.
Absolutely! Many universities offer interdisciplinary programs that allow science students to explore multiple fields. For example, a student might study a combination of biology and chemistry to understand molecular processes, or they could delve into environmental science, which integrates biology, chemistry, and geology to study the natural world. These programs encourage a broader understanding of scientific concepts and their applications.
University science programs often emphasize practical learning and research opportunities. Students can engage in laboratory work, field trips, internships, or independent research projects. These experiences enable them to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world problems, develop critical thinking skills, and gain valuable experience in their chosen scientific disciplines. Additionally, many science degrees offer professional placement years, allowing students to work in industry or research settings.







