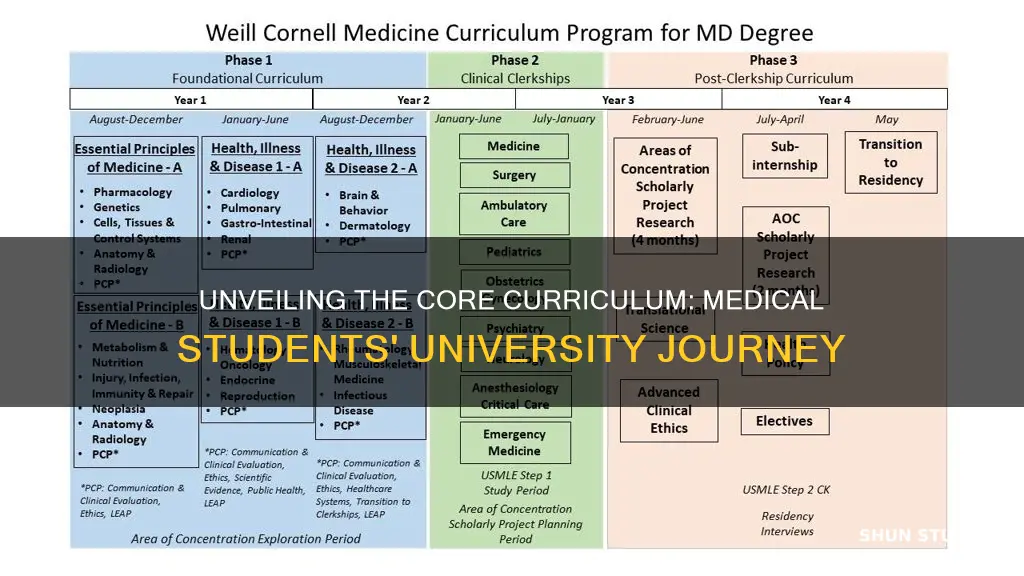
Medical students embark on an intensive and rigorous academic journey during their university years, delving into a vast array of subjects that form the foundation of medical practice. Their curriculum encompasses a broad spectrum of disciplines, including anatomy, physiology, pathology, pharmacology, and microbiology, each providing essential insights into the human body and its intricate systems. These foundational sciences are complemented by clinical studies, where students gain hands-on experience in hospitals and clinics, learning to diagnose and treat patients under the guidance of experienced physicians. The program also covers ethics, medical law, and research methodologies, ensuring students are well-equipped to navigate the complex landscape of healthcare. This comprehensive education equips future doctors with the knowledge and skills necessary to provide quality patient care and contribute to advancements in medical science.
What You'll Learn
- Anatomy: Detailed study of the body's structures, organs, and systems
- Physiology: Understanding how body systems function and interact
- Pathology: Examination of diseases, their causes, and effects on tissues
- Pharmacology: Study of drugs, their actions, and therapeutic uses
- Clinical Skills: Hands-on training in patient examination and diagnosis

Anatomy: Detailed study of the body's structures, organs, and systems
The study of anatomy is a fundamental and essential part of a medical student's university curriculum. It involves an in-depth exploration of the human body's intricate structures, organs, and systems, providing a comprehensive understanding of how the body functions and how diseases can affect these structures. This subject is crucial as it forms the basis for diagnosing and treating various medical conditions.
In the anatomy curriculum, students delve into the microscopic examination of tissues, learning about the cellular composition and function. They then progress to studying larger structures, such as the skeletal system, which includes bones, joints, and associated muscles. This part of the course often involves detailed dissections of cadavers, allowing students to visualize and understand the three-dimensional relationships between different body parts. By examining the intricate details of each bone and its attachments, students gain a profound appreciation for the body's architecture.
Moving on, the study of organs and organ systems is a significant aspect of anatomy. Medical students explore the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, and other vital organs, learning their functions, blood supply, and connections to other systems. For instance, the cardiovascular system is dissected to understand the heart's anatomy, including its chambers, valves, and electrical conduction system. This knowledge is critical for understanding how the body transports oxygen and nutrients while also learning about the impact of diseases on these vital organs.
The curriculum also covers the nervous system, which is crucial for understanding sensory perception, motor control, and cognitive functions. Students learn about the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, and how they contribute to the body's ability to process information and respond to stimuli. Furthermore, the study of the endocrine system is essential, as it involves understanding how hormones regulate various bodily functions, from metabolism to growth and development.
In summary, the detailed study of anatomy in medical university education is a comprehensive journey through the human body. It equips students with the knowledge to identify and understand the intricate structures and systems that make up the body, enabling them to diagnose and treat patients effectively. This subject is a cornerstone of medical education, providing a solid foundation for future clinical practice.
Race in Student Selection: Ethical or Not?
You may want to see also

Physiology: Understanding how body systems function and interact
The study of physiology is a fundamental aspect of a medical student's curriculum, offering a comprehensive understanding of the intricate workings of the human body. It delves into the mechanisms that govern the normal functioning of various body systems, providing a solid foundation for future clinical practice. Medical students embark on a journey to explore the complex interplay between different physiological systems, ensuring they grasp the concepts that underpin health and disease.
In the realm of physiology, students are introduced to the concept of homeostasis, the body's remarkable ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. This principle is crucial as it helps students comprehend how the body regulates its functions, from temperature control to blood glucose management. For instance, understanding how the endocrine system secretes hormones to regulate metabolism is essential. Students learn that the pancreas releases insulin to lower blood sugar levels, while glucagon raises it, illustrating the delicate balance the body maintains.
The study of physiology also involves examining the structure and function of individual organs and systems. For instance, the cardiovascular system's role in transporting oxygen and nutrients throughout the body is vital. Medical students learn about the heart's structure, its electrical activity, and the process of blood flow. They explore how the respiratory system facilitates gas exchange, ensuring oxygen reaches body tissues and carbon dioxide is expelled. This detailed understanding of each system's unique contributions to overall health is a cornerstone of medical education.
Furthermore, physiology education encourages students to appreciate the interconnectedness of body systems. For example, the nervous and endocrine systems work in harmony to regulate various bodily functions. The nervous system, with its rapid responses, controls immediate actions, while the endocrine system provides long-term regulation through hormones. Students learn that disruptions in one system can have cascading effects on others, emphasizing the holistic nature of human physiology.
Through comprehensive lectures, practical demonstrations, and clinical rotations, medical students gain hands-on experience in applying physiological knowledge. They observe how different body systems interact in real-world scenarios, from the impact of hypertension on the cardiovascular system to the effects of diabetes on the entire metabolic pathway. This practical approach ensures that students not only understand the theory but also grasp the clinical implications of physiological processes.
Student IDs: Universal or Unique?
You may want to see also

Pathology: Examination of diseases, their causes, and effects on tissues
Pathology is a fundamental branch of medicine that involves the scientific study of diseases and their impact on the body. Medical students delve into this discipline to understand the intricate relationship between diseases, their underlying causes, and the subsequent effects on various tissues and organs. The examination of diseases is a critical aspect of medical education, as it forms the basis for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient care.
In the context of pathology, medical students learn to identify and analyze the various signs and symptoms associated with different diseases. This includes understanding the pathophysiology, which is the study of the biological mechanisms that lead to the development and progression of diseases. By grasping these concepts, students can differentiate between various conditions, ensuring they provide appropriate medical care. For instance, they might examine the differences between infectious and inflammatory diseases, each requiring distinct diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
The study of pathology also involves the microscopic examination of tissues and cells. Medical students are trained to use advanced laboratory techniques, such as histology and cytology, to visualize and interpret cellular changes. This microscopic analysis allows them to identify disease processes at a cellular level, providing valuable insights into the structural and functional alterations caused by various pathogens or disease states. For example, they may observe the presence of abnormal cells in a biopsy sample, indicating cancerous growth, or detect signs of inflammation in a tissue section.
Furthermore, pathology education extends beyond the identification of diseases to understanding their causes and consequences. Medical students explore the various factors that contribute to the onset and progression of diseases, including genetic predispositions, environmental influences, and lifestyle factors. This comprehensive understanding enables them to develop strategies for disease prevention and management. They learn to interpret clinical data, perform autopsies, and analyze patient records to determine the underlying causes of diseases, which is crucial for evidence-based practice.
In summary, pathology plays a pivotal role in medical education, offering students a comprehensive understanding of diseases and their impact on the body. Through the examination of diseases, their causes, and effects on tissues, medical students gain the necessary knowledge and skills to diagnose, treat, and manage various medical conditions effectively. This discipline equips future physicians with the ability to interpret complex medical data, make informed decisions, and provide patient-centered care.
Unveiling the Nickname: Seattle U Students' Unique Title
You may want to see also

Pharmacology: Study of drugs, their actions, and therapeutic uses
Pharmacology is a cornerstone of medical education, offering students a deep understanding of how drugs interact with the human body to treat and manage diseases. This discipline is crucial as it equips future healthcare professionals with the knowledge to prescribe and administer medications effectively and safely. The study of pharmacology involves exploring the intricate relationship between drugs and the body's biological systems, aiming to optimize patient care.
In the realm of pharmacology, medical students delve into the mechanisms of drug action, which can be broadly categorized into several types. One fundamental aspect is pharmacodynamics, which examines the effects of drugs on the body's physiological processes. This includes understanding how drugs interact with receptors, enzymes, and transporters to elicit therapeutic responses. For instance, students learn about agonists and antagonists, which are drugs that either activate or block receptor sites, respectively, and how these interactions lead to changes in cellular function.
Another critical area of study is pharmacokinetics, which focuses on the body's handling of drugs. This includes the processes of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). Medical students learn how the body processes and eliminates medications, which is vital for determining appropriate dosing regimens and understanding potential side effects. For example, they explore how different routes of administration (oral, intravenous, etc.) impact drug absorption and bioavailability.
The curriculum also covers therapeutic drug monitoring, a practice that involves regularly assessing drug levels in the body to ensure optimal and safe treatment. This is particularly important for drugs with a narrow therapeutic index, where the difference between effective and toxic doses is small. Students learn to interpret laboratory results and use this information to adjust dosing regimens, ensuring patients receive the right amount of medication at the right time.
Furthermore, pharmacology education extends to the study of drug interactions, which can significantly impact patient outcomes. Medical students are taught to recognize potential drug-drug and drug-food interactions, as these can alter drug efficacy and increase the risk of adverse effects. This knowledge is essential for prescribing medications safely and effectively, especially in complex patient cases. The study of pharmacology also includes an understanding of pharmacogenomics, which explores how genetic variations influence drug response, offering personalized medicine approaches.
USC Summer Programs: A Popular Choice for Students
You may want to see also

Clinical Skills: Hands-on training in patient examination and diagnosis
Medical students embark on a rigorous journey during their university years, delving into a comprehensive curriculum that equips them with the necessary skills and knowledge to become competent healthcare professionals. One of the pivotal aspects of their education is clinical skills training, which focuses on hands-on patient examination and diagnosis. This practical approach allows students to apply their theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios, fostering a deeper understanding of clinical medicine.
During clinical skills training, students engage in various hands-on activities that simulate patient interactions. They learn the art of physical examination, which involves a systematic approach to assessing a patient's overall health. This includes mastering techniques for palpation, auscultation, and visual inspection, enabling them to detect abnormalities and gather essential clinical data. For instance, students practice taking a patient's pulse, listening to heart and lung sounds, and examining the abdomen to identify any tenderness or masses. These skills are honed through supervised practice, ensuring students can perform these tasks accurately and efficiently.
The training also emphasizes the importance of communication and patient interaction. Medical students learn to build rapport with patients, explain medical conditions in understandable terms, and actively listen to their concerns. Effective communication is vital for obtaining accurate histories, understanding patient expectations, and establishing trust. Role-playing and simulated patient encounters are common methods used to enhance these skills, allowing students to practice their bedside manner and adaptability in different clinical scenarios.
In addition to physical examination, students are taught to interpret clinical findings and make diagnoses. They learn to analyze symptoms, consider differentials, and formulate differential diagnoses. This process involves critical thinking, problem-solving, and the application of medical knowledge. Through case discussions and problem-based learning, students develop the ability to integrate various clinical clues to reach accurate diagnoses, often with the guidance and feedback of experienced mentors.
Clinical skills training is an essential component of medical education, as it bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. It empowers students to become competent examiners and diagnosticians, preparing them for the challenges they will face in clinical settings. This hands-on approach not only enhances their technical skills but also fosters confidence and a deeper appreciation for the complexities of patient care. As medical students progress through their curriculum, they gradually transition from passive observers to active participants in the healthcare process, ultimately shaping their future roles as compassionate and skilled physicians.
Study in Italy: University of Milan Tuition for International Students
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Medical students embark on an extensive journey through various scientific disciplines, including anatomy, physiology, pathology, pharmacology, and biochemistry. This foundation is crucial for understanding the human body and its functions.
Clinical rotations are a significant part of medical education. Students gain hands-on experience by working with patients under the supervision of experienced physicians. They learn to take medical histories, perform physical examinations, and interpret diagnostic tests.
Absolutely! Medical ethics is a core component of the curriculum. Students explore ethical dilemmas, patient rights, confidentiality, and the responsibilities of healthcare professionals. These courses ensure future doctors are well-versed in providing ethical and compassionate care.
While medical students primarily focus on common diseases and conditions, they also learn about rare and exotic diseases. This knowledge is essential for differential diagnosis and understanding the full spectrum of human pathology. It equips students with the skills to recognize and manage unusual cases.
Research and scientific writing are integral parts of medical education. Students are encouraged to engage in research projects, often collaborating with faculty members. They learn to design experiments, analyze data, and communicate their findings effectively through scientific publications.







