University dropout rates are a cause for concern, with statistics showing that a significant number of students leave higher education without graduating. In the US, the college dropout rate for undergraduate students is 32.9%, with 57% of students enrolled in college not graduating after six years. 33% of these students drop out entirely, while 24% remain enrolled but do not complete their degree within six years. The situation is similar in other countries, such as Canada, where at least eight universities have a completion rate below 60%.
There are various reasons for students dropping out of university. Financial issues are a significant factor, with two in five students citing money problems as the main reason for leaving. Other reasons include the inability to balance work and school, academic difficulties, mental health issues, and a lack of support from the institution.
The consequences of dropping out can be significant, with dropouts facing higher unemployment rates and increased likelihood of defaulting on student loans. They may also experience self-esteem issues and feel less capable of achieving their dreams.
What You'll Learn

Financial reasons
University can be expensive, and many students drop out due to financial reasons. The cost of tuition fees, textbooks, accommodation, and study devices can add up quickly, causing financial stress and leading to students leaving their studies.
In the UK, four in five students (78%) say that money worries cause them significant stress, with 60% avoiding social activities, and 46% too anxious to check their bank balance. A similar pattern is seen in the US, where 59% of students considered dropping out due to financial stress, and 78% reported a negative impact on their mental health.
In South Africa, the average cost of sending an individual to university in 2023 was R55,900, and this number is expected to rise to R95,700 by 2030. This increase in the cost of tertiary education is one of the main reasons why students drop out.
Financial struggles are not limited to tuition fees and textbooks. Many students also need to work part-time to support themselves, and the demands of a job can affect their ability to commit to their studies. Additionally, family commitments can add to the pressure, and students often struggle to manage their time and resources effectively.
Financial literacy plays a crucial role in a student's ability to stay in university. In the US, only 21% of students felt incredibly confident in understanding the details of their financial aid offer letter. This highlights the importance of financial education and support for students to help them make informed decisions about their education and future.
Xavier University's Student Population: A Comprehensive Overview
You may want to see also

Work and family commitments
Balancing work and family commitments is a significant reason why students drop out of university. Many students have to work part-time to keep up with the financial demands of their degrees. However, the time spent on their jobs affects their ability to commit to their studies. When family commitments are added to the mix, many students are unable to cope with the various pressures, often resulting in them leaving university.
According to a study by the University of Texas at El Paso and Borough of Manhattan Community College, students with preschool-aged children had only about 10 hours per day for sleeping, eating, leisure activities, and schoolwork after paid work, housework, and childcare. On the other hand, students without children had roughly 21 hours for the same tasks. The study also found that parents of preschool-aged children were about twice as likely to drop out of college as those without children.
Financial struggles are often intertwined with work and family commitments. In the United States, 30% of students identified money issues as their reason for leaving college. Childcare expenses can be particularly challenging for student-parents, and existing financial aid is often insufficient to cover these costs. As a result, student-parents may have to work more, leaving them with less time for studying and increasing the likelihood of dropping out.
To avoid dropping out due to work and family commitments, students should ensure they have the capacity to manage their responsibilities and prioritize their studies. Communicating with employers and universities is essential, as many jobs offer study leave, and universities may have support centres, daycare facilities, or other resources to help students balance their commitments.
Computer Requirements for Catholic University Students: What You Need
You may want to see also

Academic unpreparedness
One of the main challenges students face is the need to develop stronger study habits and time management skills. In university, the workload can be much heavier than in high school, and students are expected to take more initiative in their learning. This can be a shock to some students, who may have relied on structured learning environments in the past. As a result, they may find themselves overwhelmed and unable to keep up with the pace of their courses.
Additionally, critical thinking and analytical skills are crucial for success in higher education. University courses often require students to engage with complex concepts and ideas, and those who lack these skills may struggle to understand the material or produce the level of work expected of them. This can lead to a sense of frustration and discouragement, ultimately contributing to the decision to drop out.
Another aspect of academic unpreparedness is the lack of proper academic support. Some students may not have access to adequate resources, such as tutoring services or study groups, to help them succeed in their courses. They may also lack guidance in choosing the right courses or majors that align with their interests and abilities, leading to a sense of disengagement or burnout.
Furthermore, the social and personal challenges of university life can also contribute to academic unpreparedness. Students may find themselves struggling to balance their academic responsibilities with their social lives, extracurricular activities, or even part-time jobs. This can lead to a decline in academic performance and, ultimately, a decision to leave school.
To address academic unpreparedness and reduce dropout rates, universities can play a crucial role by providing comprehensive support services. This includes offering academic advising, study skills workshops, tutoring programs, and mental health resources to help students navigate the challenges of university life successfully.
Central Florida University: Grad Scholarships Available?
You may want to see also

Social life
University life is a significant shift from the high school experience, and many students are unprepared for the freedom and independence that comes with it. This newfound freedom can lead to students overindulging in the social aspects of university life, including alcohol and drug use. When this happens, students can struggle to keep up with their academics and other stressors of university life, which can lead to failing grades and, ultimately, dropping out.
To keep their social life in check, students must learn to prioritise their studies. This means declining invitations to social events or rescheduling them so that they can focus on upcoming tests and assignments. It is essential to understand that having a social life is an essential part of the university experience and can contribute positively to a student's overall well-being. Therefore, if a student has exams or assignments coming up, they can ask their friends to meet at a different time or organise their schedule to prioritise their university commitments first.
Additionally, students who are first-generation university attendees may feel the pressure of this new freedom even more intensely, as they cannot lean on their parents' experiences for guidance. It is crucial for these students to find support structures, such as fellow students going through similar experiences or university counsellors, to help them navigate the challenges of university life.
Furthermore, students with existing mental health challenges may find it more difficult to manage their social life at university. Prioritising mental health and seeking support from the university's mental health resources can be crucial in helping these students stay on track with their studies and avoid dropping out.
Parking Availability for Students at Middlesex University
You may want to see also

Choosing the wrong course
One of the main reasons students drop out is that they find the workload difficult to handle. This can be attributed to a variety of factors, including a lack of preparation for the academic demands of university, a lack of discipline, or personal issues. In some cases, students may realise that university life is not for them, and that is okay. It is important for students to explore other options and find something they are passionate about if university is not the right fit.
Additionally, the transition to university can be a challenging period for many students. The academic and social expectations at university are often very different from those at high school, and students may struggle to adapt. This can lead to students feeling overwhelmed and burnt out, especially if they are also trying to live on their own for the first time.
To reduce the likelihood of students dropping out due to choosing the wrong course, it is important for universities to provide adequate support and resources. This includes offering academic guidance, mental health services, and practical advice on adjusting to university life. It is also crucial for students to have realistic expectations of university and to recognise that it is normal to struggle at times.
Furthermore, it is important to note that dropping out of university does not mean failure. While it may be disappointing, it can be an opportunity for students to re-evaluate their goals and make a change that better aligns with their interests and strengths.
Manchester Metropolitan University: A Large Student Community
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The college dropout rate in the US is around 32.9% as of 2025.
23.3% of first-time, full-time freshmen dropped out of college between the fall semesters of 2021 and 2022.
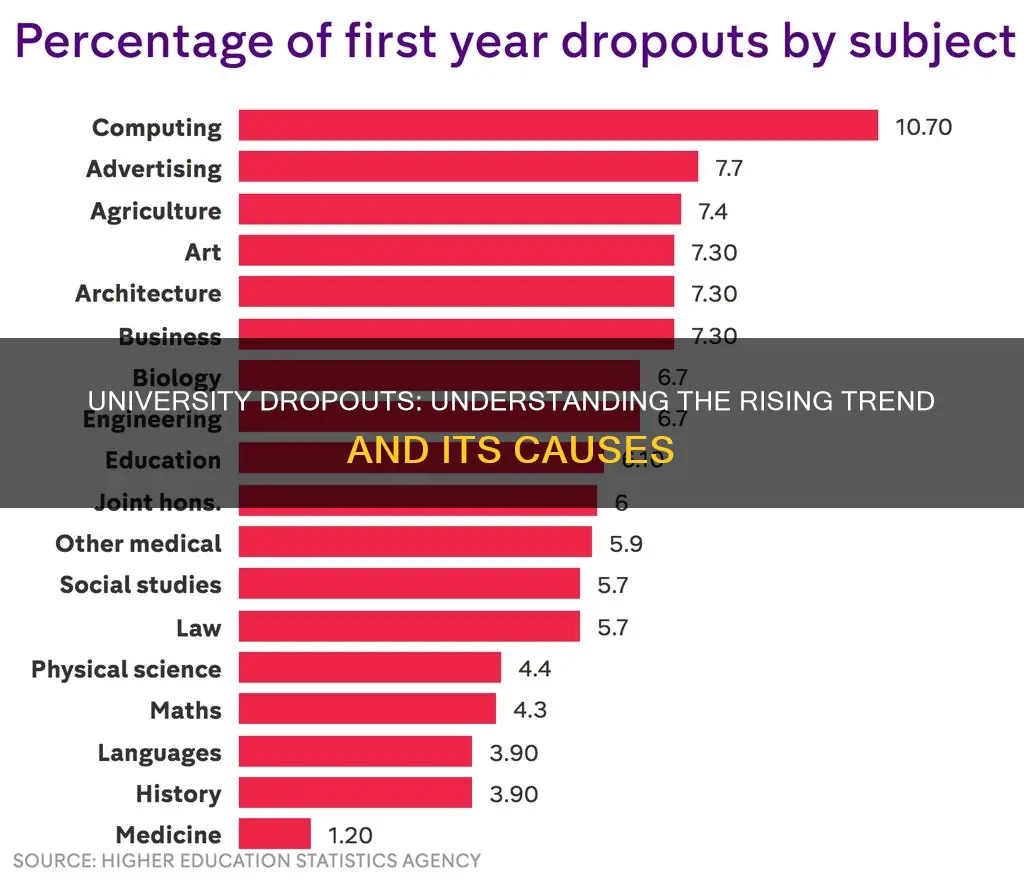
Computer science has the highest dropout rate at 10.7%, followed by advertising at 7.7%.
Men have higher dropout rates than women in public universities and private nonprofit colleges. However, women have higher dropout rates in private for-profit colleges.







