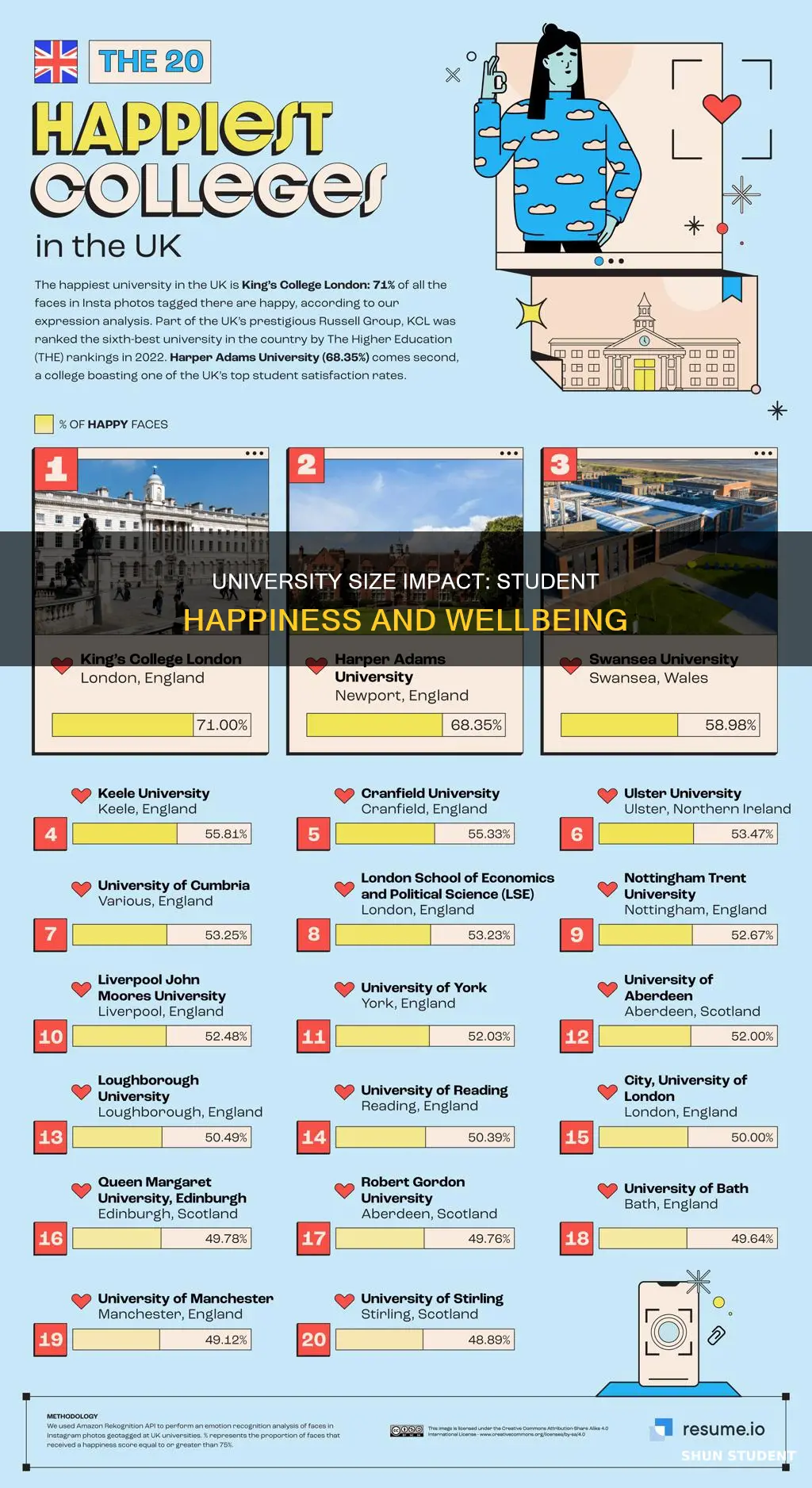
University student happiness is a growing research area in economics, with studies exploring the various factors that influence students' well-being. While some research focuses on the individual, familial, and social aspects that contribute to happiness, other studies examine the role of university size and endowment funds in student satisfaction. The size of a university's undergraduate enrollment can indicate student satisfaction, as larger enrollments suggest that more students desire to attend, reflecting their contentment with the institution. Additionally, universities with larger endowments tend to have higher student satisfaction due to increased spending on academic and cultural enhancements. However, it is worth noting that the allocation of endowment funds, rather than their sheer size, may be the primary driver of student happiness.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| University size | Larger universities tend to have higher student satisfaction due to their higher demand, admissions yields, and retention rates. |
| Student endowment funds | Universities with larger endowments tend to have higher student satisfaction due to better admissions rates, admissions yields, retention rates, and graduation rates. |
| Personal factors | Health, academic performance, sleep schedule, and relationships are all associated with happiness. |
| Familial factors | Frequent contact with family and harmonious relationships with parents enhance happiness. |
| Social factors | Social relationships, resources, and the educational environment are important for student happiness. |
| Individual factors | Age, gender, grade level, and academic level can influence happiness. |
| Family environment | A positive family environment contributes to student happiness. |
| Academic pressures | University students face academic, life, and employment pressures that can affect their happiness. |
What You'll Learn

Student happiness and the role of university endowment size
University is a critical period for personal growth, and student happiness is of great significance for self-growth, family togetherness, social stability, and national development. While there are many factors that influence student happiness, the role of university endowment size is an important consideration.
University endowment size can impact student happiness in several ways. Firstly, larger endowments can provide greater financial resources for the university, which can be used to improve various aspects of the student experience. This includes funding for teaching, research, student scholarships, maintenance and construction, and public service. For example, a larger endowment may allow a university to offer more generous financial aid packages, attracting a more diverse student body and improving access for students from lower-income backgrounds. Additionally, a well-funded university may be able to invest in upgraded facilities, such as modern libraries, state-of-the-art laboratories, or recreational spaces, all of which can enhance the student experience and contribute to their happiness.
Secondly, the size of a university's endowment can influence its institutional strategy and ambitions. A larger endowment provides a university with greater financial flexibility and stability, allowing it to plan for the long term. This can lead to more innovative and student-centric initiatives, which can positively impact student happiness. For instance, a university with a substantial endowment may be able to offer a wider range of courses, providing students with more diverse educational opportunities. Additionally, a well-endowed university may be able to attract and retain top faculty talent, ensuring that students receive a high-quality education, which can contribute to their overall satisfaction and happiness.
However, it is important to note that the relationship between university endowment size and student happiness is not always linear. While a larger endowment can provide benefits, it is not the sole determinant of a positive student experience. In fact, critics have questioned the utility of large, multi-billion-dollar endowments, suggesting that they may lead to a focus on wealth accumulation rather than the institution's core educational mission. Additionally, the impact of endowment size can depend on the number of students at the university. A large endowment spread over many students may be more limited in its effectiveness in improving student happiness, as the funds must be distributed across a wider population.
Furthermore, the impact of endowment size on student happiness can be influenced by other factors, such as the university's spending priorities and investment strategies. Universities with large endowments must carefully manage their funds to ensure they keep up with investment growth and avoid losing purchasing power. Additionally, the restrictions placed on endowment funds by donors can sometimes limit the flexibility of institutions in responding to evolving student needs or emergencies. In such cases, a large endowment may not necessarily translate directly into improved student happiness if the funds are not utilized effectively or allocated towards the right areas.
In conclusion, while university endowment size can play a role in student happiness, it is a complex relationship influenced by various factors. A larger endowment can provide benefits such as increased financial resources and stability, but it must be managed effectively and aligned with the institution's strategic priorities to positively impact students' overall well-being and satisfaction.
Southern Wesleyan University's Student Population: How Many?
You may want to see also

How student satisfaction is linked to university acceptance rates
University student happiness is influenced by a variety of factors, including personal, familial, and social factors. Research has shown that students with good health, high academic performance, and a supportive family environment tend to be happier. Additionally, academic pressures, life pressures, and employment pressures can negatively impact student happiness.
Student satisfaction, a key aspect of higher education, is influenced by institutional factors such as academic reputation, accommodation, scholarship, location, sports facilities, and safety. The quality and types of interpersonal interactions within the university community also play a role in student satisfaction.
University acceptance rates may impact student satisfaction by influencing the availability of resources and support. A higher acceptance rate may lead to increased competition for resources, potentially affecting the overall student experience. Additionally, a higher acceptance rate may result in larger class sizes, which could reduce the opportunities for individualized attention and support, potentially impacting student satisfaction.
On the other hand, a lower acceptance rate may indicate a more selective or prestigious institution, which could enhance student satisfaction by providing a sense of accomplishment and exclusivity. However, it is important to note that a lower acceptance rate may also limit the diversity of the student body, which could impact the quality of interpersonal interactions and the overall campus environment.
While university acceptance rates may have an indirect relationship with student satisfaction, it is essential to consider the interplay of various factors. The perception of happiness among university students can vary, and their life pursuits, value trade-offs, and behavioral choices can all be influenced by their conceptions of happiness. Therefore, understanding student satisfaction and its link to university acceptance rates requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account individual, familial, institutional, and societal factors.
International Students at Boston University: Who Gets Accepted?
You may want to see also

The impact of academic performance on student happiness
University is a critical period for personal growth, and the healthy growth of college students is of great significance for social development and national prosperity. However, happiness levels among university students are low, and there has been a rapid rise in the suicide rate among college students. Thus, it is important to explore the factors that influence student happiness, including the impact of academic performance on student happiness.
Academic performance has been shown to have a bidirectional relationship with student happiness. Students with high subjective well-being tend to be more successful in many areas of life, including academic success. On the other hand, experiencing negative emotions such as anxiety, distress, and shame can lead to low academic performance. Therefore, students with poor academic performance may be at risk of experiencing these negative emotions, which can further impact their overall happiness and well-being.
Research has found that academic performance is indeed one of the factors that influence university students' happiness. Students with high academic performance tend to be happier than those with poor academic performance. This may be due to the pressure and stress that university students face in their academic pursuits. Extreme stress among students can lead to poor academic performance and other negative outcomes such as health problems, addiction, and even suicidal ideation. Therefore, it is important to address students' academic performance and provide support to prevent and mitigate these risks.
In addition to academic performance, other factors that influence student happiness include personal health, familial relationships, and social factors. Students who are in good health, have a harmonious relationship with their families, and have a supportive social network tend to be happier. Gender differences have also been found to play a role, with highly academically successful boys reporting higher levels of happiness, while girls with lower academic success can still feel happy and satisfied.
Overall, academic performance can impact student happiness, and it is crucial to consider the interplay between academic performance and other factors that contribute to the overall well-being of university students. By understanding these relationships, we can develop strategies to enhance student happiness and promote their success in academic and personal pursuits.
Syracuse University: SAT Scores for Transfer Students
You may want to see also

Student happiness and the influence of family environment
University is a critical period for personal growth, and students' happiness is influenced by a variety of factors, including familial ones. Students in good health, with high academic performance, who went to sleep earlier, and who were in a loving relationship, were found to be happier. In addition, those who were in frequent contact with their families or who had a good relationship with their parents, were happier.
The family environment is a crucial factor in students' academic achievement and, consequently, their happiness. The family atmosphere, parent-child interaction, and family rules all play a role in shaping a student's academic success and overall well-being. A positive family environment, marked by effective communication, emotional support, and clear boundaries, can foster a sense of security and self-efficacy in students, contributing to their happiness.
Research has shown that the influence of family members and peer groups on adolescents' academic achievement and overall happiness can be seen as a form of 'mutual compensation'. This suggests that a supportive family environment can enhance a student's ability to navigate social relationships and peer interactions, further contributing to their happiness. Additionally, family income, family influence, parents' education, and working experiences have been found to significantly affect students' career decision self-efficacy and, ultimately, their happiness.
It is worth noting that the relationship between family environment and student happiness is complex and multifaceted. While a positive family environment can enhance happiness, family pressures and expectations can also contribute to students' academic and life pressures, affecting their overall happiness. Therefore, it is essential to consider the unique dynamics and contexts of each family when examining the influence of the family environment on student happiness.
Pursuing Chemistry PhDs: University Options and Student Numbers
You may want to see also

The effect of social relationships on student happiness
University students are subject to academic, life, and employment pressures, and their happiness is influenced by a variety of factors. Research has shown that students' perceptions of happiness are linked to their views and opinions on what happiness is and how to achieve it. These conceptions of happiness affect their life pursuits, value trade-offs, and behavioural choices.
The quality of social relationships also matters. Students who are in loving relationships and have good relationships with their parents tend to be happier. Interventions that promote social connection, such as teaching young adults about the empathy and care of their community, can help to improve student happiness. These interventions have been shown to encourage students to make new connections and build larger social networks.
In addition to social relationships, personal and familial factors also play a role in student happiness. Students who are in good health, perform well academically, and maintain a consistent sleep schedule tend to be happier.
American Universities: No Job Guarantees for Students
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
I could not find sufficient information on how university size affects student happiness. However, I can provide some general information on student happiness.
The main factors that influence student happiness include personal, familial, and social factors. Students who are in good health, have high academic performance, go to sleep earlier, and are in loving relationships tend to be happier. Additionally, those who maintain frequent contact with their families and have good relationships with their parents also report higher levels of happiness.
While some studies suggest that gender differences exist, with women generally experiencing higher states of happiness than men, other studies comparing happiness levels in students from public and private universities found no significant differences in happiness between genders.
Student happiness seems to vary across different countries and regions. For example, a survey of college students in seven countries and regions, including Australia, Canada, India, and the United States, found that students were generally happy with their college choices, with 62-67% reporting they were happy and only 13% unhappy.







