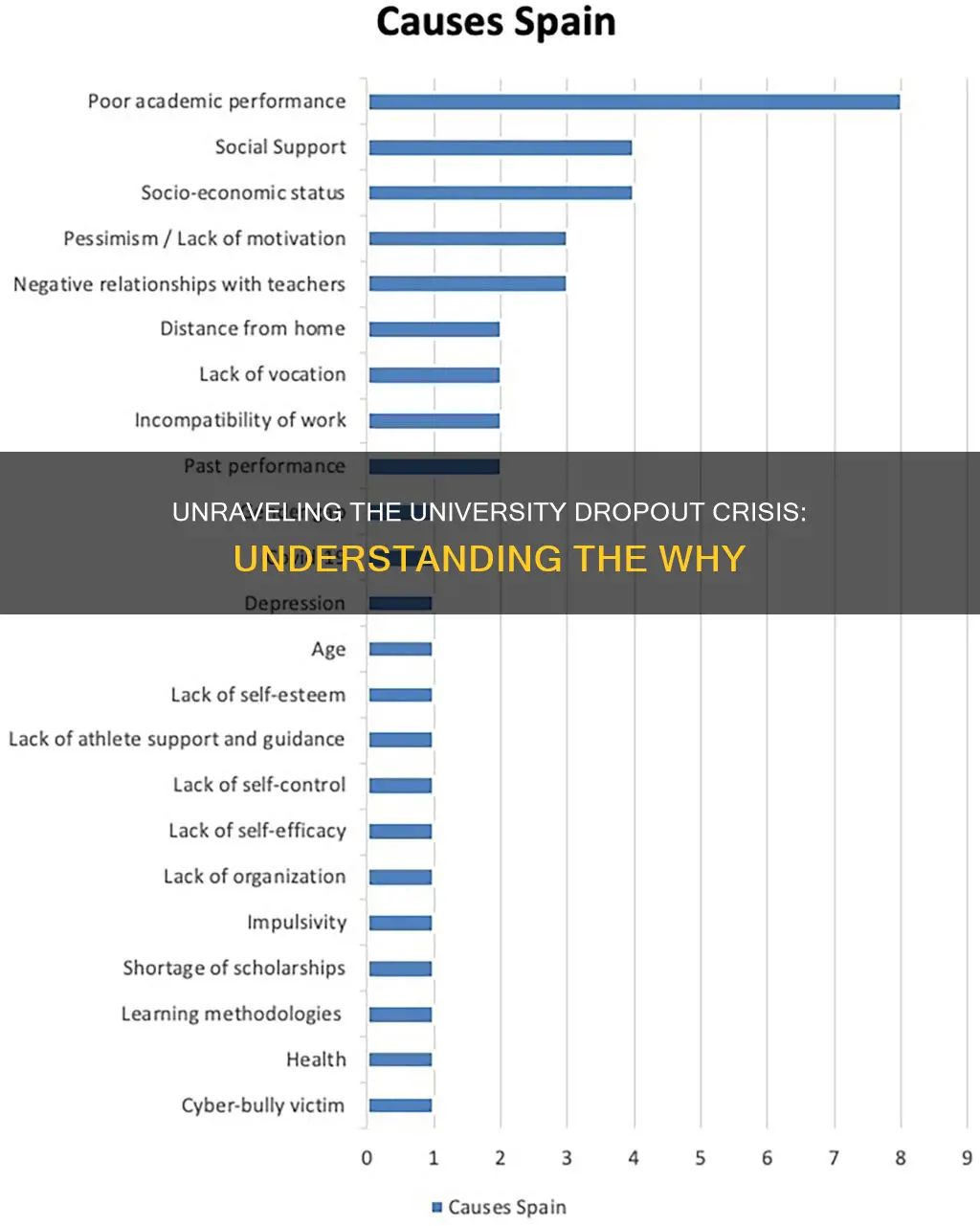
University dropout rates are a pressing issue, and understanding the reasons behind student attrition is crucial for developing effective support systems. This paragraph aims to explore the multifaceted causes that contribute to students leaving their academic pursuits. From personal challenges such as mental health issues and financial strain to systemic factors like academic pressures and lack of institutional support, the reasons are diverse. By examining these factors, we can gain insights into the complex landscape of student retention and work towards creating a more supportive and inclusive higher education environment.
What You'll Learn
- Financial Strain: Economic difficulties and inability to afford tuition and living costs
- Academic Pressure: Overwhelming workload, poor grades, and fear of failure
- Personal Issues: Family problems, health concerns, or relationship challenges
- Lack of Support: Feeling isolated, lack of academic guidance, or mentor
- External Factors: Political unrest, natural disasters, or changes in government policies

Financial Strain: Economic difficulties and inability to afford tuition and living costs
Financial strain is a significant factor that often leads students to consider dropping out of university. The rising cost of education and the subsequent financial burden can be overwhelming for many students, especially those from lower-income backgrounds. University tuition fees have been steadily increasing over the years, and for many, this represents a substantial financial commitment. On top of this, students also need to consider the costs of living, including accommodation, textbooks, transportation, and other daily expenses. These expenses can quickly add up, making it challenging for students to manage their finances effectively.
For many, the inability to afford these basic necessities can lead to a difficult decision: whether to continue their education or drop out to pursue other opportunities. The pressure to work and earn an income to support themselves and, in some cases, their families can be immense. Part-time jobs or internships might provide some financial relief, but they often interfere with study schedules and can impact academic performance. As a result, students may find themselves caught in a cycle of financial stress, where the need to work and earn money becomes a priority over their education.
Living costs, especially in urban areas, can be prohibitively expensive. Rent, utilities, and food can quickly consume a significant portion of a student's budget, leaving little room for savings or additional expenses. This financial strain can lead to a sense of desperation, where students might consider dropping out to find more stable employment or to support their families. The decision to leave university is often a last resort, as students may feel they have no other choice but to prioritize financial stability over their academic goals.
Furthermore, the stress of financial difficulties can take a toll on a student's mental health and overall well-being. The constant worry about money can lead to anxiety and depression, affecting their ability to focus on studies and engage in campus life. This can create a vicious cycle where financial strain contributes to poor academic performance, which in turn may lead to further financial struggles.
In summary, financial strain is a critical issue that can push students towards dropping out of university. The rising costs of education and living expenses, coupled with the pressure to work and earn an income, can create a challenging environment for students to thrive academically. Addressing these financial challenges is essential to supporting students' success and ensuring they have the necessary resources to complete their education.
Mature Students' University Journey: Unlocking New Opportunities
You may want to see also

Academic Pressure: Overwhelming workload, poor grades, and fear of failure
The pressure of academia can be a significant contributor to student dropout rates, especially in higher education institutions. One of the primary causes of this pressure is the overwhelming workload that students often face. University courses typically demand a heavy commitment of time and effort, requiring students to manage a vast array of assignments, projects, and exams. When the workload becomes too heavy, students may feel overwhelmed and unable to keep up, leading to increased stress and a higher likelihood of dropping out.
Poor academic performance and the fear of failure are closely linked to this issue. Students who struggle to meet the high standards set by their institutions may experience a decline in confidence and motivation. The fear of not achieving the expected grades can be paralyzing, causing anxiety and a sense of inadequacy. This fear can lead to a vicious cycle where students become increasingly anxious about their performance, affecting their ability to focus and learn effectively. As a result, they might find themselves falling behind in their studies, further exacerbating their anxiety and potentially leading to withdrawal from the course.
The fear of failure is a powerful motivator for many students, and it can drive them to work even harder to avoid disappointment. However, when this fear becomes excessive, it can have detrimental effects. Students may feel compelled to take on more than they can handle, leading to burnout and a decline in overall well-being. This can result in a loss of interest in their studies, decreased productivity, and ultimately, a higher risk of dropping out.
Managing this pressure requires a multi-faceted approach. Universities should provide comprehensive support systems to help students cope with the demands of their courses. This includes offering academic advising, tutoring services, and mental health resources to ensure students have the necessary tools to succeed. Additionally, institutions can encourage a culture of support and collaboration, where students can seek help from peers and mentors, fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility.
In conclusion, academic pressure, particularly the overwhelming workload, poor grades, and fear of failure, is a critical factor in student dropout rates. By addressing these issues through supportive institutional policies and resources, universities can create a more conducive environment for learning, helping students stay engaged and motivated throughout their academic journey.
Native Student Enrollment at Colorado State University: The Numbers
You may want to see also

Personal Issues: Family problems, health concerns, or relationship challenges
Personal issues, particularly those related to family, health, and relationships, can significantly impact a student's ability to remain enrolled in university. These challenges often require a student's full attention and can lead to a decision to leave their studies. Here's an exploration of these causes:
Family Problems: Family dynamics can be a major factor in a student's decision to drop out. This includes a variety of issues such as financial difficulties, parental or sibling pressure, or even family conflict. For instance, a student might feel compelled to support their family financially, especially if they are the primary breadwinner. This responsibility can lead to a heavy workload, leaving little time for studies. Additionally, family expectations can be a burden; parents might have high academic aspirations for their children, and when these expectations are not met, it can create a sense of failure and discourage the student from continuing their education.
Health Concerns: Physical or mental health issues can be a significant barrier to a student's academic progress. Chronic illnesses, injuries, or mental health disorders can make it difficult for a student to attend classes, complete assignments, or participate in extracurricular activities. For example, a student with a severe anxiety disorder might struggle with the stress of university life, leading to a potential dropout. Health problems can also result in frequent absences, which can negatively impact their academic standing and overall performance. In some cases, the student might need to take time off to recover, and the fear of falling behind or losing their place in the course can be a powerful motivator to leave.
Relationship Challenges: Personal relationships, including romantic partnerships, friendships, and familial bonds, can also contribute to a student's decision to drop out. A student might leave their studies due to a difficult relationship with a partner or family member, which could lead to emotional distress or a sense of isolation. For instance, a romantic relationship that is unhealthy or abusive can take a toll on a student's mental health and ability to focus on their studies. Similarly, the loss of a close friend or the strain on friendships can be detrimental. These relationships can provide a sense of support and motivation, and when they are lacking or become strained, the student might feel unsupported and less inclined to continue their university journey.
Managing these personal issues is crucial for students' well-being and academic success. It often requires a combination of support systems, such as counseling services, academic advisors, and sometimes, a temporary leave of absence to address these challenges. By recognizing and addressing these personal issues, students can develop strategies to overcome them and potentially return to their studies with a renewed sense of purpose and resilience.
University of Houston Clear Lake: Student Population Insights
You may want to see also

Lack of Support: Feeling isolated, lack of academic guidance, or mentor
The absence of a supportive network can significantly contribute to a student's decision to leave university. Many students often feel isolated, especially when they encounter challenges or face unfamiliar academic demands. This sense of isolation can be a major factor in their dropout rate. When students lack the necessary academic guidance and mentorship, they may struggle to navigate the complexities of university life.
Academic guidance is crucial for students' success. It provides them with the tools and strategies to excel in their studies. Without proper guidance, students might find themselves overwhelmed by the workload, unsure of how to approach their assignments, or lacking the skills to manage their time effectively. This can lead to increased stress, decreased motivation, and ultimately, a higher likelihood of dropping out. Mentorship, on the other hand, offers a more personal and supportive approach. Having a mentor who understands the student's goals and challenges can provide valuable insights and encouragement, helping them stay on track and make informed decisions about their academic journey.
The feeling of isolation can also stem from a lack of social connections and a sense of belonging. University life is not just about academics; it's also about building a community. Students who feel disconnected from their peers and the university environment may struggle to find their place and purpose. This isolation can lead to loneliness, decreased engagement, and a higher risk of dropping out. To combat this, universities should focus on creating a supportive and inclusive environment, ensuring that students have access to resources and opportunities to build meaningful relationships.
Addressing this issue requires a multi-faceted approach. Universities should invest in comprehensive support systems, including academic advising, mentorship programs, and social initiatives. Academic advisors can provide personalized guidance, helping students set realistic goals and develop effective study strategies. Mentorship programs can pair students with experienced individuals who can offer valuable advice and emotional support. Additionally, social events, clubs, and online communities can foster a sense of belonging and encourage students to connect with their peers.
In summary, the lack of support, whether in the form of academic guidance or a sense of community, can have a profound impact on a student's decision to continue their university journey. By recognizing and addressing these challenges, universities can create a more supportive environment, increasing the likelihood of student success and retention. It is essential to provide students with the necessary tools and resources to navigate their academic path and build a strong support network to ensure their overall well-being and long-term success.
Exploring Off-Campus Fun: Oklahoma University's Hidden Gems
You may want to see also

External Factors: Political unrest, natural disasters, or changes in government policies
The external environment can significantly impact a student's decision to leave university, and political unrest, natural disasters, and shifts in government policies are key factors to consider. Firstly, political instability can create an uncertain and unsafe atmosphere, which may prompt students to reconsider their future and potentially leave their studies. For instance, in regions affected by civil conflicts or frequent protests, the fear of violence or the desire to avoid potential risks could lead to a decrease in enrollment or even withdrawal from existing programs. Students might also face challenges in accessing educational resources, as disruptions in transportation, communication, and infrastructure can hinder their ability to attend classes regularly.
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, or floods, can have devastating effects on educational institutions and their students. These events often result in the destruction of physical infrastructure, making it impossible for universities to operate normally. When campuses are damaged or inaccessible, students may struggle to continue their education, especially if they are displaced or forced to relocate. The aftermath of a natural disaster can also lead to financial strain, as families and institutions might need to allocate resources to recovery efforts, leaving less funding for education. This can further discourage students from pursuing their academic goals.
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the higher education landscape. Changes in policies can directly impact tuition fees, financial aid, and scholarship opportunities, making it more or less affordable for students to complete their degrees. For example, if a government decides to increase tuition fees significantly, it could deter students from enrolling or force them to take on substantial debt, potentially leading to financial strain and, in some cases, dropout. Additionally, shifts in immigration policies can affect international students' ability to study abroad, as visa restrictions or changes in entry requirements might make it challenging for them to continue their education in a specific country.
In summary, external factors such as political unrest, natural disasters, and changes in government policies can significantly contribute to student dropout rates. These circumstances often create an unstable and challenging environment, impacting students' ability to access education, manage finances, and make long-term plans. Understanding these external influences is essential for educators, policymakers, and support systems to develop strategies that mitigate the risks and provide appropriate assistance to students facing such challenges.
Midwestern State University Debt: A Comprehensive Student Financial Overview
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are several factors that can contribute to a student's decision to leave their university education. These include personal issues such as mental health problems, financial difficulties, or family responsibilities. Academic challenges, like struggling to meet course requirements or feeling unsupported by the institution, can also play a significant role. Additionally, a lack of engagement with the university community, including feeling disconnected from peers, professors, or campus life, may lead to disengagement and ultimately dropping out.
Financial strain is a significant contributor to student dropout rates. The cost of higher education can be substantial, and many students take on substantial debt to fund their studies. When financial obligations become overwhelming, students may feel pressured to drop out to focus on finding employment or managing their debt. This is especially true for students from low-income backgrounds who might not have the same financial support systems as their peers.
Absolutely. Academic performance is a critical factor. Students who consistently struggle to meet course expectations or feel that the curriculum is not suited to their learning style may become discouraged and disengaged. Insufficient academic support, such as limited access to tutoring, inadequate study resources, or a lack of personalized guidance, can exacerbate these issues. When students feel they are not receiving the necessary assistance to succeed, they may be more inclined to leave their university.
The overall university experience is vital to student retention. A positive and supportive campus environment can significantly impact a student's decision to stay or leave. This includes the availability of extracurricular activities, a sense of community, and a welcoming atmosphere. Students who feel isolated, unsupported, or dissatisfied with the overall university experience may be more likely to drop out. Building a strong connection between students, faculty, and the institution is essential for fostering a sense of belonging and encouraging long-term commitment.







