Student athletes play a significant role in the university community, contributing to both academic and athletic excellence. However, their numbers and the impact they have on the overall student body are often a subject of curiosity. This paragraph aims to explore the average percentage of student athletes in universities, shedding light on the distribution and the potential implications for campus life and academic institutions.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Gender | Male: 55-60%, Female: 30-40% |
| Age | Typically younger, with a peak age range of 18-21 years |
| Academic Performance | Often higher GPA compared to non-athletes |
| Graduation Rate | Varies, but studies suggest athletes have a slightly lower rate |
| Sports Participation | Wide range, from individual sports (e.g., gymnastics) to team sports (e.g., football) |
| Scholarship Opportunities | Common, especially in sports with high recruitment |
| Social Impact | Can influence campus culture and community engagement |
| Health and Wellness | Often associated with better physical health and mental well-being |
| Recruitment and Selection | Universities use various criteria, including athletic ability and academic potential |
| Diversity | Athletes can contribute to a diverse student body |
What You'll Learn
- Demographics: Student-athletes' gender, race, and socioeconomic backgrounds
- Sports Participation: Types of sports and their popularity among student-athletes
- Academic Performance: GPA, graduation rates, and academic success of student-athletes
- Financial Aid: Scholarship amounts and sources for student-athletes
- Recruiting Practices: How universities recruit and admit student-athletes

Demographics: Student-athletes' gender, race, and socioeconomic backgrounds
The demographics of student-athletes at universities offer a fascinating insight into the diverse student body and the specific challenges and opportunities faced by this particular group. While the exact percentages can vary widely depending on the country, region, and specific institution, research provides a general overview of the typical demographics.
On average, student-athletes tend to be predominantly male, with studies indicating that around 70-80% of all student-athletes are male. This gender imbalance is often attributed to traditional societal norms and the historical association of sports with masculinity. However, it is important to note that this trend is gradually changing, with more female athletes participating in higher education and sports programs. The number of female student-athletes has been steadily increasing, and many universities are now actively promoting gender equality in sports.
In terms of race and ethnicity, student-athletes represent a diverse range of backgrounds. Research suggests that a significant portion of student-athletes are from minority ethnic groups, particularly in countries with a strong sporting culture. For instance, in the United States, African American and Hispanic student-athletes make up a substantial proportion of the student-athlete population. This diversity is often a result of affirmative action policies and initiatives aimed at increasing participation from underrepresented communities. These policies have been successful in promoting inclusivity and providing opportunities for athletes from diverse racial and ethnic backgrounds.
Socioeconomic status also plays a role in the demographics of student-athletes. Many student-athletes come from lower-income families, and their participation in sports can be a means of accessing higher education and social mobility. Sports scholarships and financial aid programs often provide a pathway for talented athletes from disadvantaged backgrounds to pursue their academic and athletic goals. However, it is worth mentioning that the socioeconomic diversity within student-athlete populations can vary, and some athletes may come from affluent families who can afford the associated costs of sports participation.
Understanding these demographics is crucial for universities and sports organizations to ensure that their programs are inclusive and accessible to a wide range of students. It also highlights the need for tailored support and resources to cater to the unique needs of student-athletes from different backgrounds, ensuring their academic and athletic success.
Unveiling the Top Asian Student Universities: A Global Perspective
You may want to see also

Sports Participation: Types of sports and their popularity among student-athletes
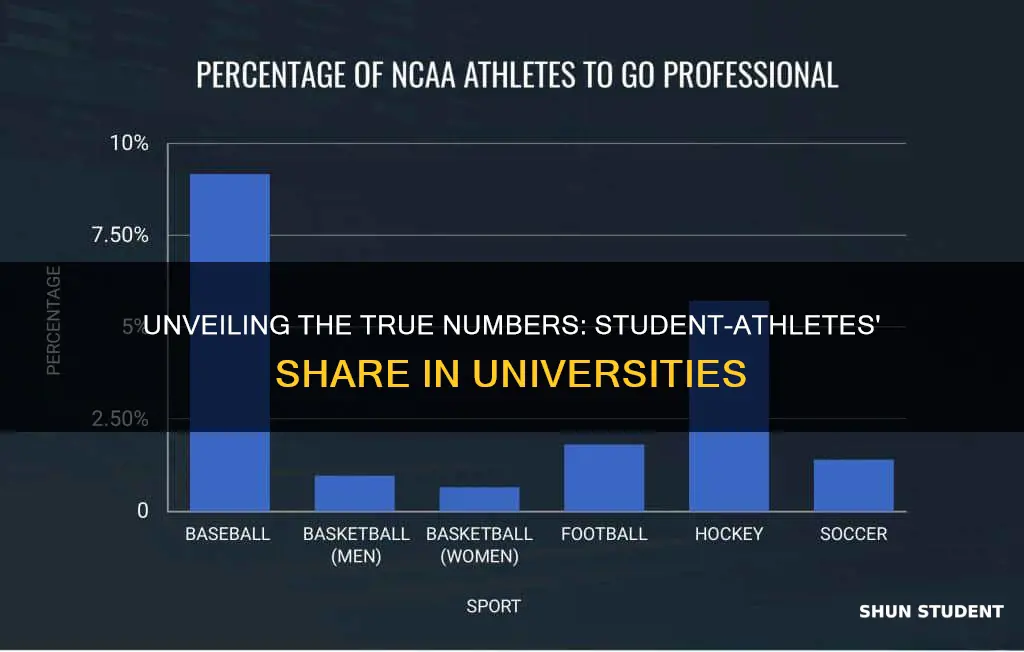
The prevalence of student-athletes in universities varies significantly across different countries and institutions, but on average, they make up a substantial portion of the student population. Research suggests that student-athletes typically account for around 10-15% of the total student body, although this percentage can be higher in certain sports-oriented universities or regions. For instance, in the United States, where college sports are incredibly popular, student-athletes can constitute a more significant proportion of the student population, often reaching or exceeding 20% in some institutions.
When examining the types of sports and their popularity among student-athletes, a diverse range of activities comes to light. Traditional team sports like football, basketball, and soccer dominate the landscape, with millions of participants worldwide. These sports offer a sense of camaraderie, intense competition, and a strong following among fans and alumni. For instance, the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) in the US organizes 24 different sports, with football and basketball being the most popular and drawing significant attention from both students and the general public.
In addition to team sports, individual sports also attract a considerable number of student-athletes. Tennis, track and field, gymnastics, and swimming are some of the individual sports that gain popularity. These sports often require a high level of skill, dedication, and personal achievement, making them appealing to athletes who excel in specific disciplines. For example, the International Tennis Federation (ITF) reports that tennis is one of the most widely played sports globally, with a significant number of university students participating in tournaments and clubs.
The popularity of certain sports can also be influenced by cultural and regional factors. For instance, sports like cricket, rugby, and field hockey are more prevalent in specific regions, such as South Asia, the United Kingdom, and parts of Africa, respectively. These sports often have a strong following among students and can contribute to the overall athletic culture of a university. Moreover, the availability of resources, such as sports facilities, coaching staff, and competitive leagues, can significantly impact the popularity and participation rates of various sports.
Understanding the popularity of different sports among student-athletes is essential for universities to cater to the interests of their student population. By offering a diverse range of sports, institutions can promote a healthy and active lifestyle, foster a sense of community, and provide opportunities for personal growth and achievement. Additionally, the popularity of sports can influence the university's reputation, enrollment numbers, and overall student satisfaction, making it a critical aspect of campus life and student engagement.
Enrolment Figures for Lawrence University: How Many Students?
You may want to see also

Academic Performance: GPA, graduation rates, and academic success of student-athletes
The academic performance of student-athletes is a critical aspect of the university experience, often under scrutiny due to the stereotype of the "jock" who excels in sports but struggles in the classroom. However, the reality is more nuanced, and understanding the academic achievements of student-athletes can provide valuable insights for educators, administrators, and policymakers.
Research indicates that student-athletes often face unique challenges that can impact their academic performance. Balancing rigorous training schedules, travel commitments, and competition demands significant time and energy, which can leave fewer hours for studying and completing assignments. Additionally, the pressure to perform in sports can lead to increased stress and anxiety, potentially affecting concentration and motivation in the classroom. As a result, it is not uncommon for student-athletes to experience lower GPAs compared to their non-athlete peers.
However, it is essential to recognize that student-athletes also bring unique strengths to the academic environment. They often possess discipline, time management skills, and a strong work ethic, which can be beneficial in various academic settings. Many student-athletes have learned to prioritize tasks, manage their schedules, and maintain focus despite the distractions of sports. These skills can contribute to their academic success and provide a competitive edge in their chosen fields of study.
Graduation rates among student-athletes are a key indicator of their academic success. Studies show that while student-athletes may start with lower GPAs, they often exhibit a strong commitment to education and a determination to graduate. This is evident in the fact that many student-athletes maintain or even improve their academic performance over time, leading to higher graduation rates compared to the general student population. The support systems in place, such as academic advisors, tutoring programs, and sports-specific academic advisors, play a crucial role in helping student-athletes overcome their challenges and achieve their educational goals.
In conclusion, the academic performance of student-athletes is a multifaceted issue. While they may face unique challenges that can impact their GPAs, they also bring valuable skills and a strong work ethic to the classroom. With the right support and resources, student-athletes can excel academically, as evidenced by their higher graduation rates. Understanding and addressing the specific needs of student-athletes can contribute to a more comprehensive and inclusive approach to education, ensuring that all students, regardless of their athletic pursuits, have the opportunity to succeed.
Enrolment Figures for Harrisburg University: A Comprehensive Overview
You may want to see also

Financial Aid: Scholarship amounts and sources for student-athletes
The financial support provided to student-athletes through scholarships is a crucial aspect of their university experience, often enabling them to pursue their athletic careers alongside their academic pursuits. The amount and source of these scholarships can vary widely depending on the university, the sport, and the athlete's performance.
On average, student-athletes account for a significant portion of the student body, with estimates ranging from 5% to 15% of the total student population. This percentage can be even higher in certain sports, such as football and basketball, where the demand for talented athletes is often high. For instance, a study conducted by the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) revealed that, on average, Division I schools receive applications from approximately 15% more prospective student-athletes than the total number of available spots. This highlights the competitive nature of the scholarship process for athletes.
Scholarship amounts can vary greatly, with some athletes receiving full-ride scholarships covering all their educational expenses, while others may receive partial scholarships that contribute towards their tuition, fees, and sometimes even living expenses. Full-ride scholarships are typically awarded to top-tier athletes who excel in their sport and often have exceptional academic credentials. These scholarships can be renewable for the duration of the athlete's eligibility, provided they maintain satisfactory academic progress. Partial scholarships, on the other hand, may cover a specific percentage of the total cost of attendance, which can range from 25% to 75%, depending on the university and the athlete's performance.
The sources of financial aid for student-athletes are diverse. Firstly, universities often provide athletic scholarships, which are awarded based on the athlete's talent and potential to contribute to the team's success. These scholarships are typically renewable for the duration of the athlete's eligibility and can cover a significant portion of their educational costs. Additionally, some universities offer need-based scholarships, which take into account the athlete's financial situation and may provide additional support. External sources of funding also play a role, including private donations, alumni contributions, and corporate sponsorships. Many student-athletes also benefit from academic scholarships, which recognize their academic achievements and provide financial support accordingly.
It is important for student-athletes to understand the scholarship process and the various sources of financial aid available to them. They should actively seek information from their university's financial aid office, athletic department, and academic advisors to ensure they are aware of all the opportunities. Additionally, maintaining a good academic standing is crucial, as it can impact the renewal of scholarships. By exploring these avenues, student-athletes can secure the necessary financial support to pursue their athletic and academic goals.
Seoul National University: Open to International Students?
You may want to see also

Recruiting Practices: How universities recruit and admit student-athletes
The process of recruiting and admitting student-athletes to universities is a complex and highly regulated system, designed to balance athletic excellence with academic integrity. This practice is a cornerstone of many sports-centric institutions, where the recruitment of talented athletes is crucial for the success of their sports programs. The average percentage of student-athletes in universities can vary significantly depending on the country and the level of competition, but it typically ranges from 10% to 20% of the total student population. This figure highlights the significant role that student-athletes play in the university's overall athletic and academic landscape.
Recruiting student-athletes involves a meticulous process that begins with identifying potential candidates. Coaches and scouts play a vital role in this phase, attending games, tournaments, and other sporting events to scout for talent. They analyze performance metrics, such as statistics, game footage, and even personal interviews, to assess the athlete's skills, potential, and fit within the team. This initial screening is followed by more in-depth evaluations, including physical assessments, medical checks, and academic reviews, to ensure the athlete meets the university's standards.
Once identified, the recruitment process involves direct communication and engagement with the prospective student-athletes and their families. Universities often host recruitment camps, showcases, and other events to provide athletes with an opportunity to showcase their skills and learn about the institution. These events are carefully organized to ensure a fair and transparent process, allowing coaches to assess the athlete's performance and personality. The university's admissions team also plays a crucial role, reviewing academic records, test scores, and other relevant information to make informed decisions.
Admissions criteria for student-athletes are often more stringent, considering both athletic and academic qualifications. Universities may have specific requirements for minimum grades, standardized test scores, and athletic performance standards. For instance, a university might require a minimum GPA or specific test scores while also assessing the athlete's potential to contribute to the team's success. This dual evaluation process ensures that admitted student-athletes are not only talented athletes but also academically capable of thriving in a university setting.
The recruitment and admission process for student-athletes is a carefully managed endeavor, requiring coordination between athletic departments, admissions offices, and often external agencies. It is a competitive and selective process, with universities aiming to build a strong athletic program while maintaining high academic standards. This balance ensures that student-athletes receive the necessary support to excel in both their sport and their academic pursuits, contributing to the overall success and reputation of the university.
Study Abroad Trends: Auburn University Students Going Global
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The percentage of student athletes in universities varies widely depending on the country, sport, and level of competition. On average, it is estimated that around 2-5% of university students are active student athletes, but this can range from less than 1% to over 10% in certain sports and institutions.
In many cases, student athletes are a small but dedicated group within the university community. They often receive specialized support and resources, such as athletic scholarships, coaching staff, and access to sports facilities. However, they typically represent a minority of the total student population, especially in universities with a strong focus on academic excellence.
No, not all universities prioritize or have the infrastructure to support athletics. Smaller institutions or those with a primary focus on academic research may have fewer or no organized sports teams. Additionally, universities with a strong emphasis on individual sports like gymnastics or tennis might have a higher percentage of student athletes compared to those with a focus on team sports.
The percentage of student athletes can vary significantly depending on the sport. For example, sports like football, basketball, and soccer often have a higher proportion of student athletes due to their popularity and the resources they attract. In contrast, individual sports like swimming, track and field, or gymnastics may have a lower percentage but still contribute a dedicated group of athletes to the university.







