Hispanics at university often face unique challenges when it comes to language learning. This paragraph introduces the topic of language study statistics among Hispanic university students, highlighting the importance of understanding language learning patterns and the potential barriers faced by this demographic. It sets the stage for further exploration of language study trends and the factors influencing language acquisition among Hispanic students.
What You'll Learn
- Language Proficiency: Examining the level of language skills among Hispanic students
- Study Patterns: Exploring the frequency and duration of language study
- Cultural Influence: How cultural factors impact language learning choices
- Academic Performance: The relationship between language study and academic achievement
- Language Usage: Understanding the practical use of foreign languages by Hispanic students

Language Proficiency: Examining the level of language skills among Hispanic students
Language proficiency is a critical aspect of academic success, especially for Hispanic students who often face unique challenges in language acquisition and retention. The ability to communicate effectively in a second language is essential for their educational journey, particularly when studying subjects like statistics, which heavily rely on precise language skills.
Research indicates that Hispanic students in higher education often encounter language barriers that impact their overall performance. These barriers can include limited English proficiency, cultural differences, and the specific demands of statistical analysis. When it comes to statistics, students must understand complex concepts and communicate them accurately, which requires a high level of language proficiency.
A study examining language skills among Hispanic university students revealed a range of proficiency levels. Many students demonstrated a strong command of the language, especially in reading and writing, but struggled with oral communication and vocabulary specific to statistical terms. This discrepancy highlights the need for targeted language support and resources tailored to the unique language requirements of statistical studies.
To address these challenges, educational institutions can implement comprehensive language programs. These programs should focus on improving vocabulary related to statistics, enhancing oral communication skills, and providing cultural sensitivity training. Additionally, offering language support services, such as tutoring and language labs, can significantly benefit Hispanic students, ensuring they have the necessary tools to succeed in their statistical studies.
Furthermore, incorporating language-focused learning strategies can be beneficial. This includes teaching students how to use language effectively for statistical analysis, such as explaining complex concepts in simple terms and providing clear, concise language for data interpretation. By enhancing language proficiency, Hispanic students can better navigate the challenges of statistical studies and achieve their academic goals.
Unlocking Udemy: Is It Free for University Students?
You may want to see also

Study Patterns: Exploring the frequency and duration of language study
Language study among Hispanic university students is a fascinating subject that delves into the academic pursuits and cultural interests of this diverse demographic. When examining the study patterns, it becomes evident that language learning among Hispanics is not solely confined to their native tongue or English but often extends to a variety of foreign languages. This exploration of language study frequency and duration provides valuable insights into the educational habits and aspirations of Hispanic students.
Research indicates that Hispanic students often engage in language learning as a means to enhance their academic and professional prospects. Many students opt to study languages that are in high demand in their respective fields or regions. For instance, Spanish, as the most widely spoken non-English language in the United States, is a popular choice for many. However, there is also a growing interest in learning other languages, such as French, German, and Mandarin, which are considered valuable assets in international communication and business. The frequency of language study among Hispanics can vary significantly, with some students dedicating a few hours a week to language classes, while others immerse themselves in language learning for several hours daily.
The duration of language study programs for Hispanic students can range from a few months to several years. Some students might take intensive language courses during the summer or as part of a study abroad program, providing them with a rapid immersion into the target language. Others may opt for more extended language learning journeys, perhaps as part of a language degree or as a prerequisite for a specific major. This variation in study duration allows students to achieve different levels of proficiency, from basic conversational skills to advanced fluency.
A key aspect of language study patterns is the influence of cultural and personal factors. Many Hispanic students are motivated by a desire to connect with their cultural heritage, improve their communication skills, or gain a competitive edge in the job market. For example, learning Spanish might be a way to strengthen ties with Spanish-speaking family members or to better understand Latin American literature and culture. On the other hand, studying Mandarin could be driven by a passion for Chinese history and cuisine or a recognition of the language's global importance in business and diplomacy.
Understanding the frequency and duration of language study among Hispanic university students is essential for educators and institutions. It helps in tailoring language programs to meet the specific needs and interests of this student population. Moreover, it can guide the development of language learning resources and support systems, ensuring that Hispanic students have the necessary tools to succeed in their language studies and beyond. By recognizing the diverse language learning patterns within the Hispanic community, educational institutions can foster a more inclusive and culturally responsive learning environment.
Christian University in Arizona: Student Population Insights
You may want to see also

Cultural Influence: How cultural factors impact language learning choices
The cultural context plays a significant role in shaping the language learning preferences of Hispanic university students. Language learning is often influenced by a combination of individual and societal factors, and for this demographic, cultural heritage and community dynamics are key considerations.
In many Hispanic communities, there is a strong emphasis on maintaining and preserving cultural identity. Spanish, the native language of most Hispanics, is a powerful symbol of cultural heritage and a means to connect with one's roots. As a result, many students may choose to study Spanish as a way to honor their cultural background and ensure that their language skills remain strong within their community. This cultural pride and the desire to contribute to the preservation of the Spanish language can be powerful motivators for language learning.
Additionally, the social and cultural environment within the university setting can impact language choices. Hispanic students might be more inclined to study languages that are commonly spoken in their region or that have cultural significance. For example, in areas with a strong Latin American influence, students might be drawn to learning languages like Portuguese, French, or even indigenous languages, which can provide a deeper connection to their cultural heritage. The availability of language courses and the presence of cultural organizations or clubs on campus can also influence these choices, as students may seek out languages that are offered or that align with their cultural interests.
Furthermore, the influence of family and community expectations cannot be overlooked. In many Hispanic families, there is a tradition of passing down language skills, and older generations may encourage their children to learn languages that were historically used in their community. This intergenerational transfer of language knowledge can significantly impact the language learning choices of Hispanic students. For instance, a student might choose to study a language like Italian or German if their family has a history of speaking these languages, even if they are not commonly studied in the university's curriculum.
Cultural identity and community engagement are powerful drivers in the language learning journey of Hispanic students. The desire to preserve cultural heritage, the influence of social and academic environments, and family traditions all contribute to the specific language choices made by this demographic. Understanding these cultural factors is essential for educators and language instructors to provide effective support and create an inclusive learning environment that respects and embraces the diverse language learning motivations of Hispanic students.
Morehouse University: Black Students Only?
You may want to see also

Academic Performance: The relationship between language study and academic achievement
The study of foreign languages has long been recognized as a valuable asset in higher education, and its impact on academic performance, particularly among Hispanic students, is an area of growing interest. Research has shown that language study can significantly influence the academic achievement of students, especially those from diverse linguistic backgrounds. When it comes to Hispanic university students, the statistics reveal a compelling narrative regarding their engagement with foreign languages and its correlation with academic success.
Hispanic students often face unique challenges in an academic setting, especially when it comes to language barriers. However, the decision to study a foreign language can be a powerful tool to overcome these obstacles. Numerous studies have indicated that language study enhances cognitive abilities, including reading, writing, and critical thinking skills, which are essential for academic excellence. For Hispanic students, learning a foreign language can provide a foundation for better understanding and communicating in their native tongue, potentially improving their overall academic performance.
The benefits of language study extend beyond the acquisition of linguistic skills. It encourages cultural awareness and sensitivity, which are crucial in today's globalized world. Hispanic students who engage in foreign language programs often develop a deeper understanding of different cultures, fostering a more inclusive and diverse learning environment. This cultural sensitivity can positively impact their academic journey, as it encourages open-mindedness and a willingness to explore diverse perspectives.
Furthermore, the study of foreign languages can have a direct impact on academic achievement. Research suggests that students who study a second language tend to perform better in various subjects, including mathematics and science. This improvement is attributed to the enhanced cognitive flexibility and problem-solving abilities that language learning cultivates. For Hispanic students, this could mean better grades, increased confidence, and a higher likelihood of pursuing advanced studies.
In conclusion, the relationship between language study and academic achievement is evident, particularly for Hispanic university students. By engaging with foreign languages, these students can improve their language proficiency, cultural understanding, and overall academic performance. The benefits of language study extend beyond the classroom, empowering students with valuable skills that will serve them throughout their educational journey and beyond. This approach to education has the potential to bridge linguistic gaps and create a more inclusive and successful learning environment for all.
Exploring Western Michigan University's Student Population
You may want to see also

Language Usage: Understanding the practical use of foreign languages by Hispanic students
The practical use of foreign languages among Hispanic students is an intriguing aspect of language study, especially in the context of university education. When examining the statistics, it becomes evident that language proficiency plays a significant role in various aspects of academic and personal development. Hispanic students often bring a rich linguistic background to their university experience, which can greatly influence their language usage and learning strategies.
In many cases, these students have a strong command of Spanish, which is their native language. However, the extent of their proficiency in other languages varies. Some students might have studied English as a second language (ESL) in their previous educational stages, while others may have learned French, German, or even indigenous languages from their cultural heritage. The diversity of language skills among Hispanic students is a testament to the complex linguistic landscape they navigate.
The practical application of these languages becomes evident in various scenarios. For instance, in a multilingual classroom, Hispanic students can facilitate communication and understanding among peers from different linguistic backgrounds. They may also contribute to the creation of a more inclusive learning environment, ensuring that all students feel represented and understood. Additionally, language skills can be a powerful tool for personal growth, enabling students to connect with their cultural roots and fostering a sense of identity.
Language proficiency also impacts academic performance. Students who are proficient in multiple languages may have an advantage in certain subjects, especially those requiring precise communication, such as science, engineering, or international relations. For example, a student with strong Spanish and English skills might excel in research projects that involve bilingual sources or contribute to cross-cultural collaborations. Moreover, language abilities can open doors to various career paths, as many professions value multilingual employees for their communication and problem-solving skills.
Understanding the language usage patterns of Hispanic students is essential for educators and institutions. It allows for the development of tailored language support programs, ensuring that students can fully utilize their linguistic strengths. This might include language exchange programs, language-focused clubs, or even language-specific academic resources. By recognizing and promoting the practical use of foreign languages, universities can enhance the overall learning experience and empower Hispanic students to become effective communicators and global citizens.
Hiring Student Grads: NSU's Approach to Student Employment
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The research primarily aims to analyze and present statistics on the languages studied by Hispanic students at universities, offering insights into their language learning patterns and preferences.
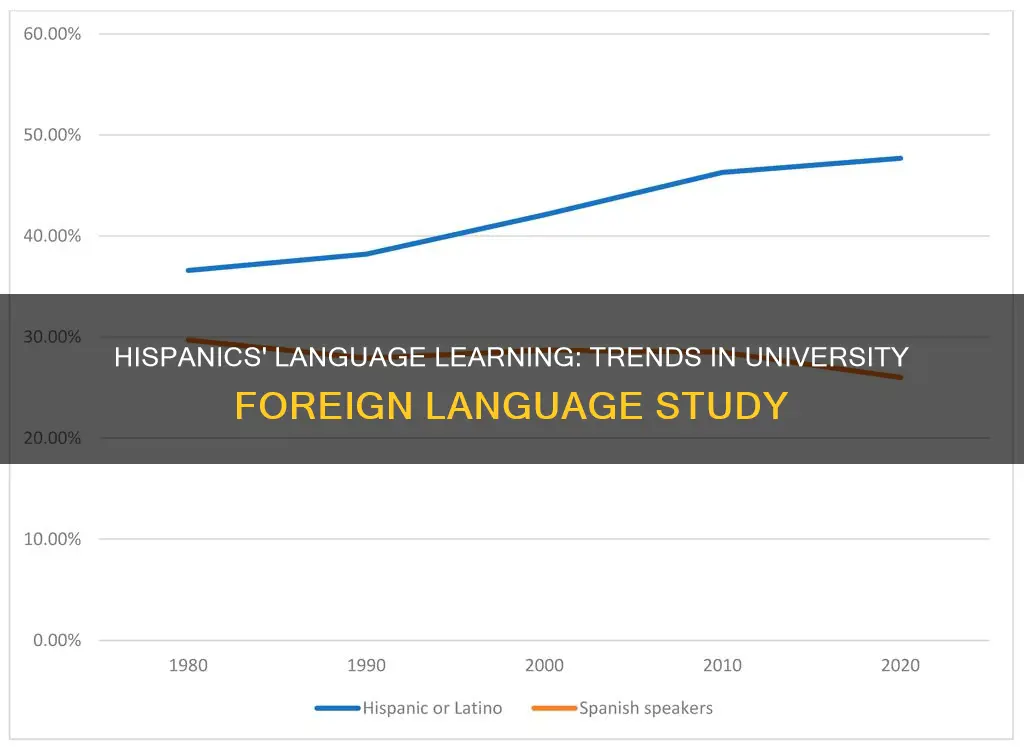
The statistics reveal that a significant portion of Hispanic students at the university have engaged in foreign language studies. Recent data indicates that approximately 75% of the Hispanic student population has taken at least one foreign language course.
Spanish is the most prevalent foreign language studied by Hispanic students, with a high enrollment rate in Spanish language courses. Additionally, there is a growing interest in learning French, Mandarin, and Arabic, reflecting a diverse language learning trend.
Cultural and familial backgrounds play a significant role in language choices. Many students opt for Spanish due to its cultural relevance and shared heritage. However, there is also a rising demand for languages that facilitate international communication, such as Mandarin and Arabic, indicating a shift towards global language learning.







