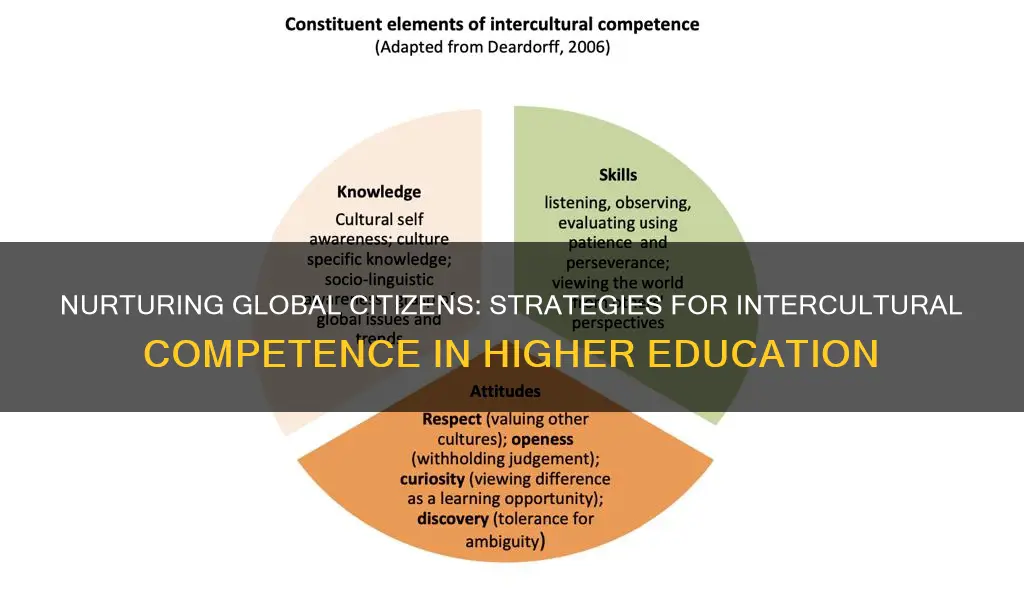
Developing intercultural competence is an essential skill for university students in today's globalized world. Intercultural competence refers to the ability to understand, communicate with, and appreciate people from different cultural backgrounds. This skill is crucial for fostering cross-cultural understanding, promoting diversity, and preparing students for a globalized society. In this article, we will explore practical strategies and approaches that can be implemented in university settings to enhance students' intercultural competence. By adopting these methods, educators can create an inclusive learning environment that encourages cultural exchange, empathy, and mutual respect among students from diverse backgrounds.
What You'll Learn
- Encourage Cross-Cultural Interactions: Foster student exchanges and collaborative projects to promote cultural understanding
- Provide Cultural Training: Offer workshops and seminars to educate students about diverse cultures and communication styles
- Create Inclusive Environments: Design curricula and campus activities that celebrate cultural diversity and encourage open dialogue
- Promote Self-Reflection: Facilitate personal growth by encouraging students to reflect on their own cultural biases and perspectives
- Support Global Citizenship: Develop programs that foster global awareness and a sense of responsibility for global issues

Encourage Cross-Cultural Interactions: Foster student exchanges and collaborative projects to promote cultural understanding
Encouraging cross-cultural interactions is a powerful strategy to enhance intercultural competence among university students. This approach involves creating opportunities for students to engage with peers from diverse cultural backgrounds, fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of different cultures. One effective method to achieve this is by implementing student exchange programs. These programs allow students to study or intern in partner universities located in different countries, providing them with a firsthand experience of another culture. During their exchange, students can immerse themselves in the local community, attend cultural events, and interact with local students, thereby gaining valuable insights into the host culture.
Additionally, collaborative projects can be designed to bring students from various cultural backgrounds together. These projects should aim to tackle real-world issues or problems that require a multidisciplinary approach. By working in teams, students can learn to appreciate different perspectives and develop skills in conflict resolution and effective communication. For instance, a project could involve designing a community service initiative that addresses a local need, requiring input from students with diverse cultural and academic backgrounds. Through this process, students learn to value and integrate different ideas, fostering a more inclusive and culturally sensitive environment.
To facilitate these cross-cultural interactions, universities should actively seek partnerships with institutions in other countries. This can be done through international office initiatives, where staff members are dedicated to promoting and organizing exchange programs and collaborative projects. Building a network of partner universities will not only provide students with more opportunities to engage in cross-cultural experiences but also enhance the university's reputation on the global stage. Furthermore, providing adequate support and resources, such as cultural orientation programs and mentorship schemes, can ensure that students feel welcomed and supported during their international experiences.
In the context of collaborative projects, it is essential to create a safe and inclusive environment where students feel comfortable sharing their cultural insights and perspectives. This can be achieved by establishing clear guidelines and expectations for respectful behavior and open dialogue. Project leaders should encourage students to reflect on their cultural assumptions and biases, promoting a more nuanced understanding of cultural differences. By doing so, students can learn to navigate and manage cultural differences effectively, developing their intercultural competence.
Lastly, the benefits of cross-cultural interactions extend beyond the individual students. By fostering these exchanges and collaborations, universities contribute to the development of a more globally-minded and culturally competent student body. This, in turn, prepares students to become active global citizens who can effectively contribute to and collaborate in an increasingly interconnected world. Thus, encouraging cross-cultural interactions through student exchanges and collaborative projects is a vital step in developing intercultural competence among university students.
American University's Semester in Washington: Student Numbers
You may want to see also

Provide Cultural Training: Offer workshops and seminars to educate students about diverse cultures and communication styles
Developing intercultural competence in university students is a crucial aspect of fostering an inclusive and global learning environment. One effective strategy to achieve this is by providing comprehensive cultural training through workshops and seminars. These educational sessions play a pivotal role in equipping students with the necessary knowledge and skills to navigate diverse cultural contexts and communicate effectively with individuals from different backgrounds.
Workshops and seminars offer a structured and interactive approach to learning. They provide a safe space for students to explore and discuss various cultural topics, often facilitated by experts or experienced educators. During these sessions, students can gain insights into the history, traditions, values, and communication norms of different cultures. For instance, a workshop on 'Understanding Asian Communication Styles' could delve into the importance of indirect communication in some Asian cultures, the use of non-verbal cues, and the impact of hierarchical structures on interpersonal interactions. By presenting such practical and culturally relevant topics, students can develop a deeper understanding of the complexities of cross-cultural communication.
The benefits of these training programs extend beyond theoretical knowledge. They encourage students to reflect on their own cultural identities and biases, fostering self-awareness and empathy. Through group discussions and role-playing activities, students can practice adapting their communication styles to different cultural contexts, enhancing their ability to build bridges across cultural divides. Moreover, workshops can provide practical tools and strategies for managing cultural misunderstandings and conflicts, ensuring that students are well-prepared for real-world interactions.
Incorporating a variety of cultural topics into the curriculum ensures a well-rounded education. This might include sessions on gender dynamics, religious practices, and the impact of colonization on indigenous cultures. By covering a broad spectrum of cultural issues, students can develop a more nuanced understanding of the world and become more adaptable in diverse settings. Additionally, offering workshops in multiple languages and with diverse facilitators can further enhance inclusivity and provide a more personalized learning experience.
The impact of these cultural training initiatives can be long-lasting. By the end of such workshops, students are more likely to feel empowered to engage with people from different backgrounds, fostering a more harmonious and respectful campus community. This, in turn, contributes to the development of global citizens who can effectively collaborate and communicate in an increasingly interconnected world. Thus, providing cultural training through workshops and seminars is a powerful step towards creating an intercultural-competent student body.
Linfield University Student Population: A Comprehensive Overview
You may want to see also

Create Inclusive Environments: Design curricula and campus activities that celebrate cultural diversity and encourage open dialogue
Developing intercultural competence in university students is a crucial aspect of fostering an inclusive and diverse learning environment. One effective approach to achieving this is by designing curricula and campus activities that actively celebrate cultural diversity and encourage open dialogue. Here are some strategies to create such inclusive environments:
Curriculum Design: When crafting your university's academic programs, ensure that courses incorporate diverse perspectives and global issues. Include case studies and examples from various cultural backgrounds to provide a well-rounded education. For instance, in history or literature classes, offer a range of texts and narratives that represent different cultures and eras. This approach helps students understand the richness of human experiences and challenges stereotypes. Additionally, consider integrating modules on cross-cultural communication, conflict resolution, and global ethics to equip students with practical skills for navigating diverse environments.
Cultural Events and Workshops: Organize a variety of campus activities that showcase and celebrate cultural diversity. Host cultural festivals, food fairs, and art exhibitions that allow students to experience different traditions and customs. These events can be organized by student clubs or in collaboration with local communities. For instance, a cultural food festival can be an opportunity to educate students about various cuisines and the cultural significance behind them. Furthermore, conduct workshops on topics like cultural sensitivity, bias awareness, and cross-cultural communication. These workshops can facilitate meaningful discussions and encourage students to share their experiences and perspectives.
Intercultural Exchange Programs: Implement exchange programs or partnerships with universities in different countries to facilitate international student mobility. These programs provide students with the opportunity to study abroad, learn from international peers, and immerse themselves in new cultural contexts. By encouraging students to engage with diverse student bodies, you foster cross-cultural understanding and empathy. Ensure that these exchange programs have a strong focus on cultural integration and provide support systems for international students to navigate their new environment.
Open Dialogue Platforms: Create safe and inclusive spaces for students to engage in open dialogue about cultural differences and similarities. This can be achieved through peer-led discussion groups, cultural forums, or online platforms where students can share their experiences and perspectives. Encourage active participation and create an environment where students feel comfortable expressing their thoughts. Facilitate these discussions by providing structured frameworks, such as the 'I-Statement' technique, which promotes clear and respectful communication. Regularly organizing such dialogue sessions can help students develop empathy, challenge their assumptions, and build a deeper understanding of different cultures.
Faculty and Staff Training: Provide training sessions for faculty and staff to enhance their understanding of cultural diversity and its impact on teaching and learning. This training should focus on raising awareness of potential biases and providing tools for creating inclusive classrooms. Equip educators with strategies to incorporate cultural perspectives into their teaching materials and methods. Additionally, encourage faculty to involve students in cultural exchange projects, where they can collaborate on research or assignments that require cross-cultural collaboration.
By implementing these strategies, universities can create curricula and campus activities that actively promote cultural diversity, encourage open dialogue, and ultimately develop intercultural competence among students. This approach not only enriches the educational experience but also prepares students to become global citizens who can effectively navigate and contribute to an increasingly interconnected world.
Unveiling Saint Francis University's Student Population: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Promote Self-Reflection: Facilitate personal growth by encouraging students to reflect on their own cultural biases and perspectives
Encouraging self-reflection is a powerful tool to foster intercultural competence among university students. This process involves creating a safe and supportive environment where students can explore their own cultural identities and biases, which is essential for understanding and respecting others' perspectives. Here's how you can promote self-reflection as a means to enhance intercultural skills:
Promote Journaling and Personal Narratives: Assign students reflective journaling tasks where they write about their personal experiences, cultural backgrounds, and how these factors influence their interactions with peers from different backgrounds. For instance, they might reflect on a recent group project and analyze their contributions, communication style, and assumptions made during the collaboration. This practice allows students to identify and challenge their own cultural biases and stereotypes, fostering a deeper understanding of their own identity.
Facilitate Peer Discussions: Organize group discussions or seminars where students can share their self-reflections with peers. Creating a platform for open dialogue encourages active listening and empathy. During these sessions, students can explore how their cultural backgrounds shape their perceptions and behaviors, and how these might differ from their classmates' experiences. By sharing personal narratives, students can learn from each other, gain insights into diverse perspectives, and develop a more nuanced understanding of cultural diversity.
Provide Cultural Awareness Training: Implement workshops or seminars that focus on cultural awareness and sensitivity. These sessions can guide students in exploring their own cultural identities and the impact of cultural differences on communication and behavior. Through interactive activities and case studies, students can reflect on how their cultural backgrounds influence their interactions and decision-making processes. This structured approach helps students become more mindful of their own biases and encourages them to consider alternative viewpoints.
Offer Feedback and Mentorship: Establish a mentorship program where experienced students or faculty members provide feedback and guidance to newcomers. This mentorship can include regular check-ins and reflective conversations, allowing mentees to share their experiences and receive feedback on their intercultural competence. By reflecting on their interactions and receiving constructive feedback, students can identify areas of improvement and develop strategies to enhance their cultural understanding and sensitivity.
By implementing these self-reflection strategies, universities can empower students to become more culturally aware, empathetic, and open-minded. This process enables students to navigate diverse environments with confidence, fostering a more inclusive and respectful campus community. It is through self-reflection that students can truly embrace the complexities of cultural diversity and develop the skills necessary to communicate and collaborate effectively in an internationalized world.
Unraveling the University Dropout Mystery: Canada's Student Challenges
You may want to see also

Support Global Citizenship: Develop programs that foster global awareness and a sense of responsibility for global issues
Developing intercultural competence in university students is a crucial aspect of preparing them to become global citizens who can navigate and contribute to an increasingly interconnected world. One effective approach to achieving this is by designing and implementing programs that foster global awareness and a sense of responsibility for global issues. Here's a detailed strategy to support global citizenship:
- Cultural Exchange Programs: Organize international student exchange initiatives where domestic and international students interact and study together. This direct exposure to diverse cultures can broaden students' perspectives and encourage empathy. During these exchanges, students can engage in cultural immersion activities, language learning, and community projects, fostering a deeper understanding of global issues and promoting cross-cultural friendships.
- Global Issues Workshops: Conduct workshops or seminars focused on various global topics such as climate change, poverty, human rights, and international conflicts. Invite guest speakers, including experts, activists, and professionals working in these fields, to share their experiences and insights. These workshops can provide a platform for students to learn about global challenges, analyze case studies, and develop critical thinking skills related to international affairs.
- Model United Nations (MUN) Conferences: MUN conferences simulate the United Nations General Assembly, allowing students to take on the roles of diplomats and negotiate solutions to global issues. This hands-on experience encourages students to research, debate, and propose policies, fostering a sense of global responsibility. MUN conferences can be organized internally or externally, providing an opportunity for students to collaborate with peers from different cultural backgrounds.
- Global Volunteer Opportunities: Partner with international organizations or local NGOs to offer volunteer programs that address global challenges. These opportunities can include environmental conservation projects, community development initiatives, or human rights advocacy. By actively participating in these programs, students can develop a sense of global citizenship, gain practical experience, and understand the impact of their actions on a global scale.
- Global Awareness Campaigns: Launch campus-wide campaigns to raise awareness about global issues and encourage student involvement. This can include organizing film screenings, panel discussions, or art exhibitions that highlight international themes. Providing resources and platforms for students to engage in open dialogue and share their perspectives can create a more informed and engaged student body.
- Mentorship Programs: Establish a mentorship system where senior students or alumni mentor international or exchange students. Mentors can guide their mentees in navigating the university experience, adapting to new cultures, and understanding the local context. This one-on-one support can help students develop intercultural competence and a sense of belonging, making them more responsible global citizens.
By implementing these programs, universities can play a pivotal role in shaping students' global perspectives and empowering them to take action. These initiatives not only enhance intercultural competence but also encourage students to become active contributors to a more peaceful and sustainable world.
Transfer Students: Full Scholarships at Rice University?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Intercultural competence refers to the ability to communicate, understand, and interact effectively with people from different cultural backgrounds. It is crucial for students as it fosters global citizenship, promotes tolerance and respect, and prepares them for an increasingly diverse and interconnected world. By developing this competence, students can enhance their cross-cultural communication skills, build meaningful relationships, and contribute to a more inclusive and harmonious society.
Students can enhance their intercultural understanding through various means. Firstly, engaging in cross-cultural exchanges and study abroad programs provides direct exposure to different cultures. Participating in cultural events, clubs, or societies on campus can also offer valuable learning opportunities. Additionally, attending workshops, seminars, or lectures on cross-cultural topics can broaden their knowledge. Reading books, articles, or research papers on cultural diversity and global issues can further contribute to their understanding.
Developing intercultural communication skills involves active learning and practice. Students can start by learning basic phrases and vocabulary in multiple languages to facilitate communication. Role-playing and simulation exercises can help them practice cultural interactions and improve their ability to adapt to different cultural norms. Encouraging open dialogue and creating safe spaces for students to share their experiences and perspectives can foster cultural sensitivity and empathy. Additionally, providing feedback and constructive criticism in a respectful manner can help students refine their communication skills.
Universities play a vital role in fostering intercultural competence. They can offer interdisciplinary courses that integrate cultural studies, language learning, and social sciences. Providing cultural immersion opportunities, such as international student exchange programs or community engagement initiatives, can expose students to diverse perspectives. Implementing cultural sensitivity training and workshops can help students recognize and overcome their biases. Moreover, creating multicultural student support networks and peer-to-peer learning environments can encourage cultural exchange and understanding.







